mirror of
https://github.moeyy.xyz/https://github.com/trekhleb/javascript-algorithms.git
synced 2024-12-26 15:11:16 +08:00
Add counting sort.
This commit is contained in:
parent
b1a613e03e
commit
0c1f6851d5
@ -80,6 +80,7 @@ a set of rules that precisely defines a sequence of operations.
|
||||
* [Merge Sort](https://github.com/trekhleb/javascript-algorithms/tree/master/src/algorithms/sorting/merge-sort)
|
||||
* [Quicksort](https://github.com/trekhleb/javascript-algorithms/tree/master/src/algorithms/sorting/quick-sort) - in-place and non-in-place implementations
|
||||
* [Shellsort](https://github.com/trekhleb/javascript-algorithms/tree/master/src/algorithms/sorting/shell-sort)
|
||||
* [Counting Sort](https://github.com/trekhleb/javascript-algorithms/tree/master/src/algorithms/sorting/counting-sort)
|
||||
* **Tree**
|
||||
* [Depth-First Search](https://github.com/trekhleb/javascript-algorithms/tree/master/src/algorithms/tree/depth-first-search) (DFS)
|
||||
* [Breadth-First Search](https://github.com/trekhleb/javascript-algorithms/tree/master/src/algorithms/tree/breadth-first-search) (BFS)
|
||||
@ -225,3 +226,4 @@ Below is the list of some of the most used Big O notations and their performance
|
||||
| **Merge sort** | n log(n) | n log(n) | n log(n) | n | Yes |
|
||||
| **Quick sort** | n log(n) | n log(n) | n^2 | log(n) | No |
|
||||
| **Shell sort** | n log(n) | depends on gap sequence | n (log(n))^2 | 1 | No |
|
||||
| **Counting sort** | n + r | n + r | n + r | n + r | Yes |
|
||||
|
||||
@ -11,6 +11,7 @@ export class SortTester {
|
||||
expect(sorter.sort([1])).toEqual([1]);
|
||||
expect(sorter.sort([1, 2])).toEqual([1, 2]);
|
||||
expect(sorter.sort([2, 1])).toEqual([1, 2]);
|
||||
expect(sorter.sort([3, 4, 2, 1, 0, 0, 4, 3, 4, 2])).toEqual([0, 0, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4]);
|
||||
expect(sorter.sort(sortedArr)).toEqual(sortedArr);
|
||||
expect(sorter.sort(reverseArr)).toEqual(sortedArr);
|
||||
expect(sorter.sort(notSortedArr)).toEqual(sortedArr);
|
||||
|
||||
69
src/algorithms/sorting/counting-sort/CountingSort.js
Normal file
69
src/algorithms/sorting/counting-sort/CountingSort.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,69 @@
|
||||
import Sort from '../Sort';
|
||||
|
||||
export default class CountingSort extends Sort {
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @param {number[]} originalArray
|
||||
* @param {number} [biggestElement]
|
||||
*/
|
||||
sort(originalArray, biggestElement = 0) {
|
||||
// Detect biggest element in array in order to build in order to build
|
||||
// number bucket array later.
|
||||
let detectedBiggestElement = biggestElement;
|
||||
if (!detectedBiggestElement) {
|
||||
originalArray.forEach((element) => {
|
||||
// Visit element.
|
||||
this.callbacks.visitingCallback(element);
|
||||
|
||||
if (this.comparator.greaterThan(element, detectedBiggestElement)) {
|
||||
detectedBiggestElement = element;
|
||||
}
|
||||
});
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Init buckets array.
|
||||
// This array will hold frequency of each number from originalArray.
|
||||
const buckets = Array(detectedBiggestElement + 1).fill(0);
|
||||
originalArray.forEach((element) => {
|
||||
// Visit element.
|
||||
this.callbacks.visitingCallback(element);
|
||||
|
||||
buckets[element] += 1;
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
// Add previous frequencies to the current one for each number in bucket
|
||||
// to detect how many numbers less then current one should be standing to
|
||||
// the left of current one.
|
||||
for (let bucketIndex = 1; bucketIndex < buckets.length; bucketIndex += 1) {
|
||||
buckets[bucketIndex] += buckets[bucketIndex - 1];
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Now let's shift frequencies to the right so that they show correct numbers.
|
||||
// I.e. if we won't shift right than the value of buckets[5] will display how many
|
||||
// elements less than 5 should be placed to the left of 5 in sorted array
|
||||
// INCLUDING 5th. After shifting though this number will not include 5th anymore.
|
||||
buckets.pop();
|
||||
buckets.unshift(0);
|
||||
|
||||
// Now let's assemble sorted array.
|
||||
const sortedArray = Array(originalArray.length).fill(null);
|
||||
for (let elementIndex = 0; elementIndex < originalArray.length; elementIndex += 1) {
|
||||
// Get the element that we want to put into correct sorted position.
|
||||
const element = originalArray[elementIndex];
|
||||
|
||||
// Visit element.
|
||||
this.callbacks.visitingCallback(element);
|
||||
|
||||
// Get correct position of this element in sorted array.
|
||||
const elementSortedPosition = buckets[element];
|
||||
|
||||
// Put element into correct position in sorted array.
|
||||
sortedArray[elementSortedPosition] = element;
|
||||
|
||||
// Increase position of current element in the bucket for future correct placements.
|
||||
buckets[element] += 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Return sorted array.
|
||||
return sortedArray;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
61
src/algorithms/sorting/counting-sort/README.md
Normal file
61
src/algorithms/sorting/counting-sort/README.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
|
||||
# Counting Sort
|
||||
|
||||
In computer science, **counting sort** is an algorithm for sorting
|
||||
a collection of objects according to keys that are small integers;
|
||||
that is, it is an integer sorting algorithm. It operates by
|
||||
counting the number of objects that have each distinct key value,
|
||||
and using arithmetic on those counts to determine the positions
|
||||
of each key value in the output sequence. Its running time is
|
||||
linear in the number of items and the difference between the
|
||||
maximum and minimum key values, so it is only suitable for direct
|
||||
use in situations where the variation in keys is not significantly
|
||||
greater than the number of items. However, it is often used as a
|
||||
subroutine in another sorting algorithm, radix sort, that can
|
||||
handle larger keys more efficiently.
|
||||
|
||||
Because counting sort uses key values as indexes into an array,
|
||||
it is not a comparison sort, and the `Ω(n log n)` lower bound for
|
||||
comparison sorting does not apply to it. Bucket sort may be used
|
||||
for many of the same tasks as counting sort, with a similar time
|
||||
analysis; however, compared to counting sort, bucket sort requires
|
||||
linked lists, dynamic arrays or a large amount of preallocated
|
||||
memory to hold the sets of items within each bucket, whereas
|
||||
counting sort instead stores a single number (the count of items)
|
||||
per bucket.
|
||||
|
||||
Counting sorting works best when the range of numbers for each array
|
||||
element is very small.
|
||||
|
||||
## Algorithm
|
||||
|
||||
**Step I**
|
||||
|
||||
In first step we calculate the count of all the elements of the
|
||||
input array `A`. Then Store the result in the count array `C`.
|
||||
The way we count is depected below.
|
||||
|
||||
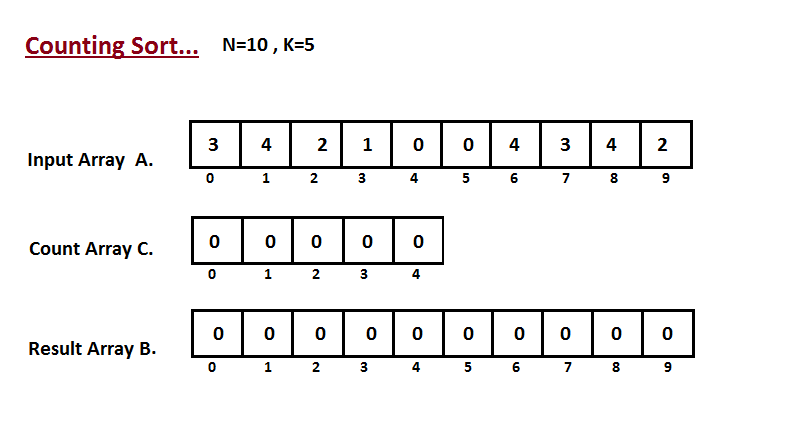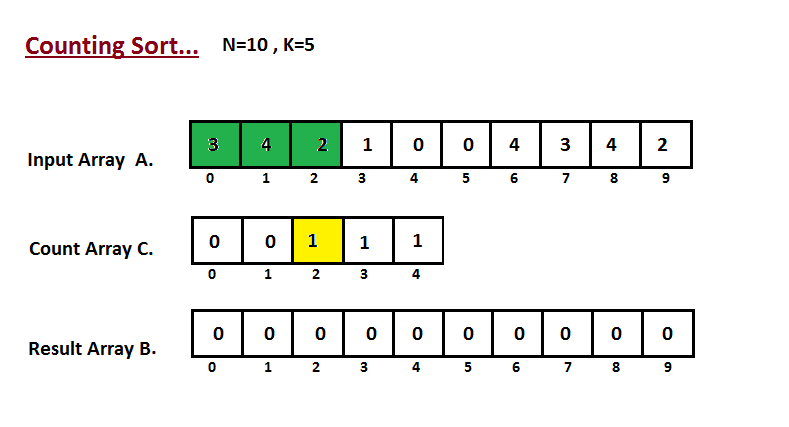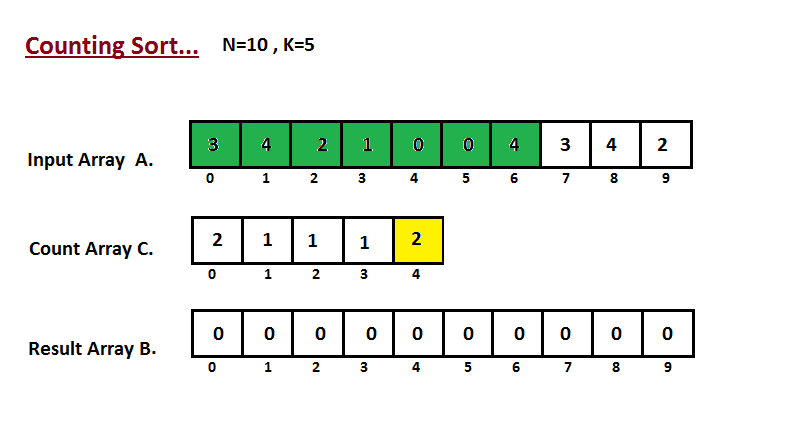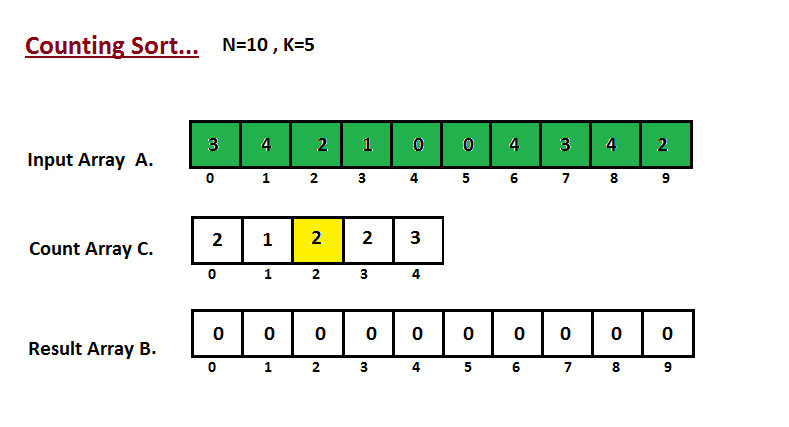
|
||||
|
||||
**Step II**
|
||||
|
||||
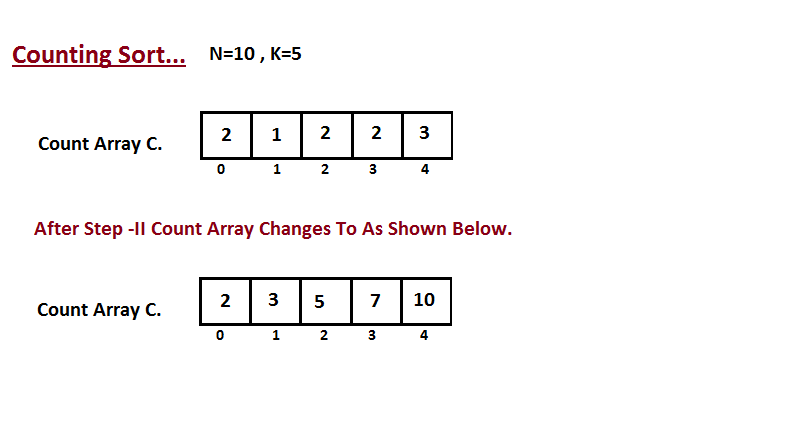
In second step we calculate how many elements exist in the input
|
||||
array `A` which are less than or equals for the given index.
|
||||
`Ci` = numbers of elements less than or equals to `i` in input array.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**Step III**
|
||||
|
||||
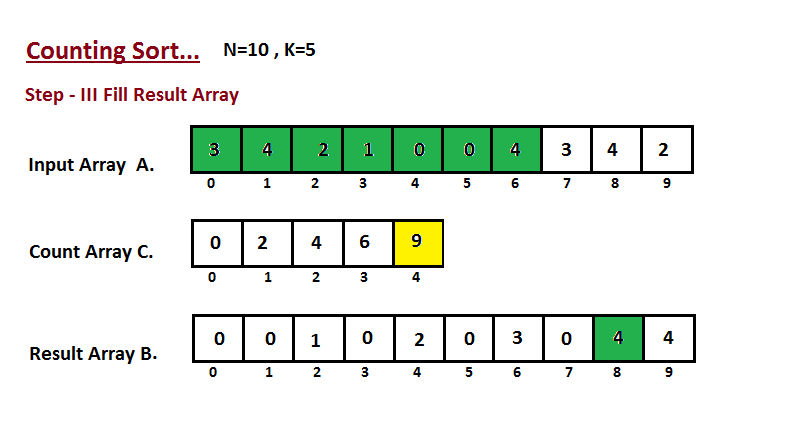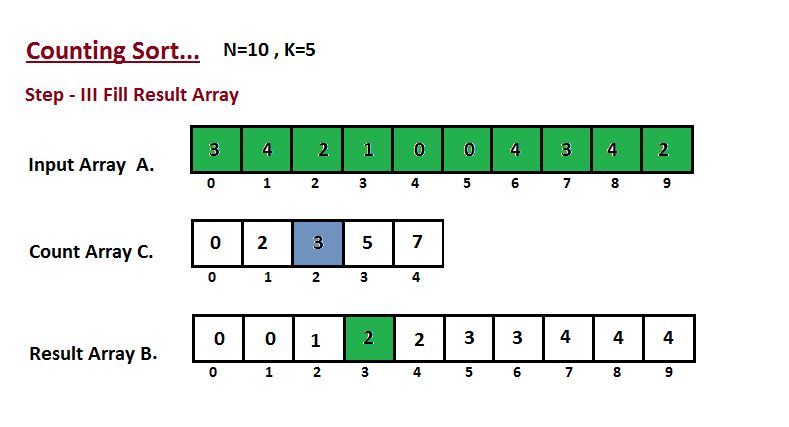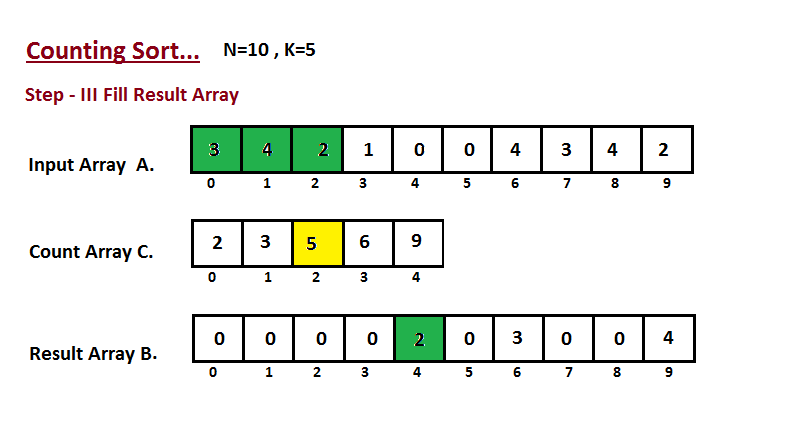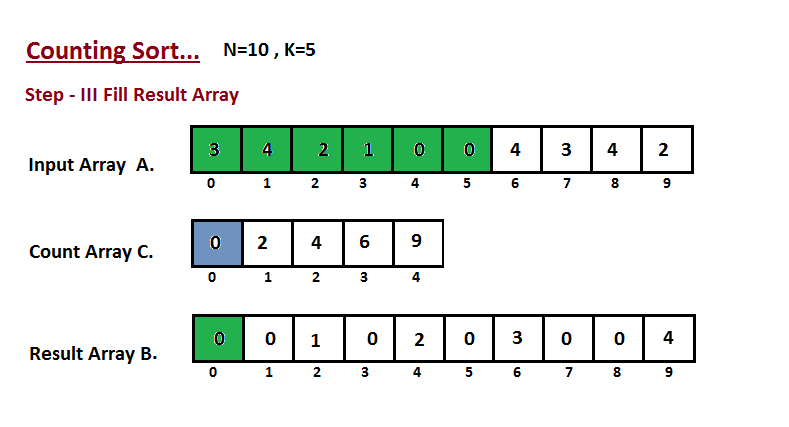
In this step we place the input array `A` element at sorted
|
||||
position by taking help of constructed count array `C` ,i.e what
|
||||
we constructed in step two. We used the result array `B` to store
|
||||
the sorted elements. Here we handled the index of `B` start from
|
||||
zero.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## References
|
||||
|
||||
- [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Counting_sort)
|
||||
- [YouTube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OKd534EWcdk&index=61&t=0s&list=PLLXdhg_r2hKA7DPDsunoDZ-Z769jWn4R8)
|
||||
- [EfficientAlgorithms](https://efficientalgorithms.blogspot.com/2016/09/lenear-sorting-counting-sort.html)
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,69 @@
|
||||
import CountingSort from '../CountingSort';
|
||||
import {
|
||||
equalArr,
|
||||
notSortedArr,
|
||||
reverseArr,
|
||||
sortedArr,
|
||||
SortTester,
|
||||
} from '../../SortTester';
|
||||
|
||||
// Complexity constants.
|
||||
const SORTED_ARRAY_VISITING_COUNT = 60;
|
||||
const NOT_SORTED_ARRAY_VISITING_COUNT = 60;
|
||||
const REVERSE_SORTED_ARRAY_VISITING_COUNT = 60;
|
||||
const EQUAL_ARRAY_VISITING_COUNT = 60;
|
||||
|
||||
describe('CountingSort', () => {
|
||||
it('should sort array', () => {
|
||||
SortTester.testSort(CountingSort);
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
it('should allow to use specify maximum integer value in array to make sorting faster', () => {
|
||||
const visitingCallback = jest.fn();
|
||||
const sorter = new CountingSort({ visitingCallback });
|
||||
|
||||
// Detect biggest number in array in prior.
|
||||
const biggestElement = notSortedArr.reduce((accumulator, element) => {
|
||||
return element > accumulator ? element : accumulator;
|
||||
}, 0);
|
||||
|
||||
const sortedArray = sorter.sort(notSortedArr, biggestElement);
|
||||
|
||||
expect(sortedArray).toEqual(sortedArr);
|
||||
// Normally visitingCallback is being called 60 times but in this case
|
||||
// it should be called only 40 times.
|
||||
expect(visitingCallback).toHaveBeenCalledTimes(40);
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
it('should visit EQUAL array element specified number of times', () => {
|
||||
SortTester.testAlgorithmTimeComplexity(
|
||||
CountingSort,
|
||||
equalArr,
|
||||
EQUAL_ARRAY_VISITING_COUNT,
|
||||
);
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
it('should visit SORTED array element specified number of times', () => {
|
||||
SortTester.testAlgorithmTimeComplexity(
|
||||
CountingSort,
|
||||
sortedArr,
|
||||
SORTED_ARRAY_VISITING_COUNT,
|
||||
);
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
it('should visit NOT SORTED array element specified number of times', () => {
|
||||
SortTester.testAlgorithmTimeComplexity(
|
||||
CountingSort,
|
||||
notSortedArr,
|
||||
NOT_SORTED_ARRAY_VISITING_COUNT,
|
||||
);
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
it('should visit REVERSE SORTED array element specified number of times', () => {
|
||||
SortTester.testAlgorithmTimeComplexity(
|
||||
CountingSort,
|
||||
reverseArr,
|
||||
REVERSE_SORTED_ARRAY_VISITING_COUNT,
|
||||
);
|
||||
});
|
||||
});
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user