mirror of
https://github.moeyy.xyz/https://github.com/trekhleb/javascript-algorithms.git
synced 2024-12-25 22:46:20 +08:00
Add Tarjan's algorithm.
This commit is contained in:
parent
21d4144e5a
commit
25703c37ac
@ -72,7 +72,8 @@
|
||||
* [Prim’s Algorithm](https://github.com/trekhleb/javascript-algorithms/tree/master/src/algorithms/graph/prim) - finding Minimum Spanning Tree (MST) for weighted undirected graph
|
||||
* [Kruskal’s Algorithm](https://github.com/trekhleb/javascript-algorithms/tree/master/src/algorithms/graph/kruskal) - finding Minimum Spanning Tree (MST) for weighted undirected graph
|
||||
* [Topological Sorting](https://github.com/trekhleb/javascript-algorithms/tree/master/src/algorithms/graph/topological-sorting) - DFS method
|
||||
* [Articulation Points](https://github.com/trekhleb/javascript-algorithms/tree/master/src/algorithms/graph/articulation-points) - Tarjan's algorithm
|
||||
* [Articulation Points](https://github.com/trekhleb/javascript-algorithms/tree/master/src/algorithms/graph/articulation-points) - Tarjan's algorithm (DFS based)
|
||||
* [Bridges](https://github.com/trekhleb/javascript-algorithms/tree/master/src/algorithms/graph/bridges) - DFS based algorithm
|
||||
* [Eulerian Path and Eulerian Circuit](https://github.com/trekhleb/javascript-algorithms/tree/master/src/algorithms/graph/eulerian-path)
|
||||
* Strongly Connected Component algorithm
|
||||
* Shortest Path Faster Algorithm (SPFA)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ class VisitMetadata {
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Tarjan's algorithm for rinding articulation points in graph.
|
||||
* Tarjan's algorithm for finding articulation points in graph.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* @param {Graph} graph
|
||||
* @return {GraphVertex[]}
|
||||
|
||||
26
src/algorithms/graph/bridges/README.md
Normal file
26
src/algorithms/graph/bridges/README.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,26 @@
|
||||
# Bridges in Graph
|
||||
|
||||
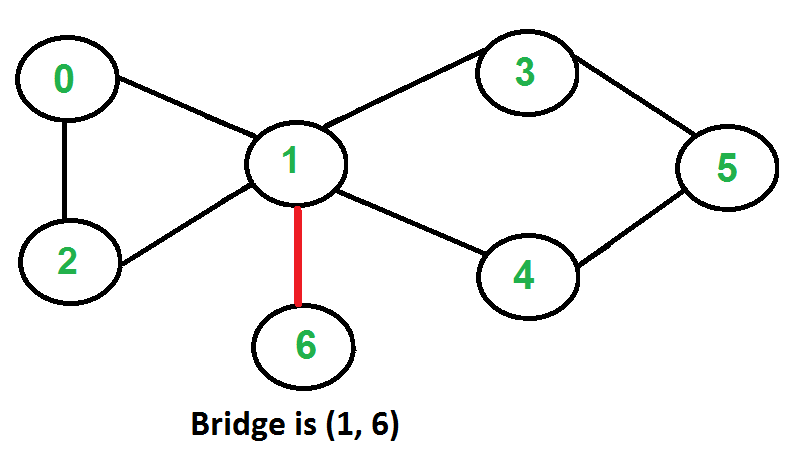
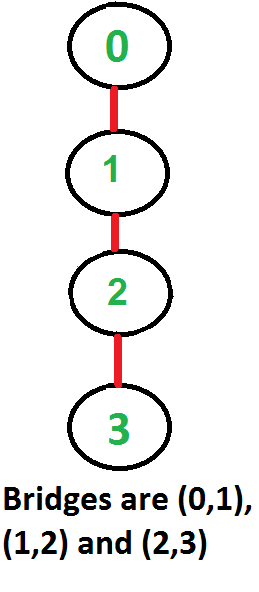
In graph theory, a **bridge**, **isthmus**, **cut-edge**, or **cut arc** is an edge
|
||||
of a graph whose deletion increases its number of connected components. Equivalently,
|
||||
an edge is a bridge if and only if it is not contained in any cycle. A graph is said
|
||||
to be bridgeless or isthmus-free if it contains no bridges.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
A graph with 16 vertices and 6 bridges (highlighted in red)
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
An undirected connected graph with no cut edges
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## References
|
||||
|
||||
- [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bridge_%28graph_theory%29#Tarjan.27s_Bridge-finding_algorithm)
|
||||
- [GeeksForGeeks](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/bridge-in-a-graph/)
|
||||
- [GeeksForGeeks on YouTube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?time_continue=110&v=thLQYBlz2DM)
|
||||
203
src/algorithms/graph/bridges/__test__/graphBridges.test.js
Normal file
203
src/algorithms/graph/bridges/__test__/graphBridges.test.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,203 @@
|
||||
import GraphVertex from '../../../../data-structures/graph/GraphVertex';
|
||||
import GraphEdge from '../../../../data-structures/graph/GraphEdge';
|
||||
import Graph from '../../../../data-structures/graph/Graph';
|
||||
import graphBridges from '../graphBridges';
|
||||
|
||||
describe('graphBridges', () => {
|
||||
it('should find bridges in simple graph', () => {
|
||||
const vertexA = new GraphVertex('A');
|
||||
const vertexB = new GraphVertex('B');
|
||||
const vertexC = new GraphVertex('C');
|
||||
const vertexD = new GraphVertex('D');
|
||||
|
||||
const edgeAB = new GraphEdge(vertexA, vertexB);
|
||||
const edgeBC = new GraphEdge(vertexB, vertexC);
|
||||
const edgeCD = new GraphEdge(vertexC, vertexD);
|
||||
|
||||
const graph = new Graph();
|
||||
|
||||
graph
|
||||
.addEdge(edgeAB)
|
||||
.addEdge(edgeBC)
|
||||
.addEdge(edgeCD);
|
||||
|
||||
const bridges = graphBridges(graph);
|
||||
|
||||
expect(bridges.length).toBe(3);
|
||||
expect(bridges[0].getKey()).toBe(edgeCD.getKey());
|
||||
expect(bridges[1].getKey()).toBe(edgeBC.getKey());
|
||||
expect(bridges[2].getKey()).toBe(edgeAB.getKey());
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
it('should find bridges in simple graph with back edge', () => {
|
||||
const vertexA = new GraphVertex('A');
|
||||
const vertexB = new GraphVertex('B');
|
||||
const vertexC = new GraphVertex('C');
|
||||
const vertexD = new GraphVertex('D');
|
||||
|
||||
const edgeAB = new GraphEdge(vertexA, vertexB);
|
||||
const edgeBC = new GraphEdge(vertexB, vertexC);
|
||||
const edgeCD = new GraphEdge(vertexC, vertexD);
|
||||
const edgeAC = new GraphEdge(vertexA, vertexC);
|
||||
|
||||
const graph = new Graph();
|
||||
|
||||
graph
|
||||
.addEdge(edgeAB)
|
||||
.addEdge(edgeAC)
|
||||
.addEdge(edgeBC)
|
||||
.addEdge(edgeCD);
|
||||
|
||||
const bridges = graphBridges(graph);
|
||||
|
||||
expect(bridges.length).toBe(1);
|
||||
expect(bridges[0].getKey()).toBe(edgeCD.getKey());
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
it('should find bridges in graph', () => {
|
||||
const vertexA = new GraphVertex('A');
|
||||
const vertexB = new GraphVertex('B');
|
||||
const vertexC = new GraphVertex('C');
|
||||
const vertexD = new GraphVertex('D');
|
||||
const vertexE = new GraphVertex('E');
|
||||
const vertexF = new GraphVertex('F');
|
||||
const vertexG = new GraphVertex('G');
|
||||
const vertexH = new GraphVertex('H');
|
||||
|
||||
const edgeAB = new GraphEdge(vertexA, vertexB);
|
||||
const edgeBC = new GraphEdge(vertexB, vertexC);
|
||||
const edgeAC = new GraphEdge(vertexA, vertexC);
|
||||
const edgeCD = new GraphEdge(vertexC, vertexD);
|
||||
const edgeDE = new GraphEdge(vertexD, vertexE);
|
||||
const edgeEG = new GraphEdge(vertexE, vertexG);
|
||||
const edgeEF = new GraphEdge(vertexE, vertexF);
|
||||
const edgeGF = new GraphEdge(vertexG, vertexF);
|
||||
const edgeFH = new GraphEdge(vertexF, vertexH);
|
||||
|
||||
const graph = new Graph();
|
||||
|
||||
graph
|
||||
.addEdge(edgeAB)
|
||||
.addEdge(edgeBC)
|
||||
.addEdge(edgeAC)
|
||||
.addEdge(edgeCD)
|
||||
.addEdge(edgeDE)
|
||||
.addEdge(edgeEG)
|
||||
.addEdge(edgeEF)
|
||||
.addEdge(edgeGF)
|
||||
.addEdge(edgeFH);
|
||||
|
||||
const bridges = graphBridges(graph);
|
||||
|
||||
expect(bridges.length).toBe(3);
|
||||
expect(bridges[0].getKey()).toBe(edgeFH.getKey());
|
||||
expect(bridges[1].getKey()).toBe(edgeDE.getKey());
|
||||
expect(bridges[2].getKey()).toBe(edgeCD.getKey());
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
it('should find bridges in graph starting with different root vertex', () => {
|
||||
const vertexA = new GraphVertex('A');
|
||||
const vertexB = new GraphVertex('B');
|
||||
const vertexC = new GraphVertex('C');
|
||||
const vertexD = new GraphVertex('D');
|
||||
const vertexE = new GraphVertex('E');
|
||||
const vertexF = new GraphVertex('F');
|
||||
const vertexG = new GraphVertex('G');
|
||||
const vertexH = new GraphVertex('H');
|
||||
|
||||
const edgeAB = new GraphEdge(vertexA, vertexB);
|
||||
const edgeBC = new GraphEdge(vertexB, vertexC);
|
||||
const edgeAC = new GraphEdge(vertexA, vertexC);
|
||||
const edgeCD = new GraphEdge(vertexC, vertexD);
|
||||
const edgeDE = new GraphEdge(vertexD, vertexE);
|
||||
const edgeEG = new GraphEdge(vertexE, vertexG);
|
||||
const edgeEF = new GraphEdge(vertexE, vertexF);
|
||||
const edgeGF = new GraphEdge(vertexG, vertexF);
|
||||
const edgeFH = new GraphEdge(vertexF, vertexH);
|
||||
|
||||
const graph = new Graph();
|
||||
|
||||
graph
|
||||
.addEdge(edgeDE)
|
||||
.addEdge(edgeAB)
|
||||
.addEdge(edgeBC)
|
||||
.addEdge(edgeAC)
|
||||
.addEdge(edgeCD)
|
||||
.addEdge(edgeEG)
|
||||
.addEdge(edgeEF)
|
||||
.addEdge(edgeGF)
|
||||
.addEdge(edgeFH);
|
||||
|
||||
const bridges = graphBridges(graph);
|
||||
|
||||
expect(bridges.length).toBe(3);
|
||||
expect(bridges[0].getKey()).toBe(edgeFH.getKey());
|
||||
expect(bridges[1].getKey()).toBe(edgeDE.getKey());
|
||||
expect(bridges[2].getKey()).toBe(edgeCD.getKey());
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
it('should find bridges in yet another graph #1', () => {
|
||||
const vertexA = new GraphVertex('A');
|
||||
const vertexB = new GraphVertex('B');
|
||||
const vertexC = new GraphVertex('C');
|
||||
const vertexD = new GraphVertex('D');
|
||||
const vertexE = new GraphVertex('E');
|
||||
|
||||
const edgeAB = new GraphEdge(vertexA, vertexB);
|
||||
const edgeAC = new GraphEdge(vertexA, vertexC);
|
||||
const edgeBC = new GraphEdge(vertexB, vertexC);
|
||||
const edgeCD = new GraphEdge(vertexC, vertexD);
|
||||
const edgeDE = new GraphEdge(vertexD, vertexE);
|
||||
|
||||
const graph = new Graph();
|
||||
|
||||
graph
|
||||
.addEdge(edgeAB)
|
||||
.addEdge(edgeAC)
|
||||
.addEdge(edgeBC)
|
||||
.addEdge(edgeCD)
|
||||
.addEdge(edgeDE);
|
||||
|
||||
const bridges = graphBridges(graph);
|
||||
|
||||
expect(bridges.length).toBe(2);
|
||||
expect(bridges[0].getKey()).toBe(edgeDE.getKey());
|
||||
expect(bridges[1].getKey()).toBe(edgeCD.getKey());
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
it('should find bridges in yet another graph #2', () => {
|
||||
const vertexA = new GraphVertex('A');
|
||||
const vertexB = new GraphVertex('B');
|
||||
const vertexC = new GraphVertex('C');
|
||||
const vertexD = new GraphVertex('D');
|
||||
const vertexE = new GraphVertex('E');
|
||||
const vertexF = new GraphVertex('F');
|
||||
const vertexG = new GraphVertex('G');
|
||||
|
||||
const edgeAB = new GraphEdge(vertexA, vertexB);
|
||||
const edgeAC = new GraphEdge(vertexA, vertexC);
|
||||
const edgeBC = new GraphEdge(vertexB, vertexC);
|
||||
const edgeCD = new GraphEdge(vertexC, vertexD);
|
||||
const edgeCE = new GraphEdge(vertexC, vertexE);
|
||||
const edgeCF = new GraphEdge(vertexC, vertexF);
|
||||
const edgeEG = new GraphEdge(vertexE, vertexG);
|
||||
const edgeFG = new GraphEdge(vertexF, vertexG);
|
||||
|
||||
const graph = new Graph();
|
||||
|
||||
graph
|
||||
.addEdge(edgeAB)
|
||||
.addEdge(edgeAC)
|
||||
.addEdge(edgeBC)
|
||||
.addEdge(edgeCD)
|
||||
.addEdge(edgeCE)
|
||||
.addEdge(edgeCF)
|
||||
.addEdge(edgeEG)
|
||||
.addEdge(edgeFG);
|
||||
|
||||
const bridges = graphBridges(graph);
|
||||
|
||||
expect(bridges.length).toBe(1);
|
||||
expect(bridges[0].getKey()).toBe(edgeCD.getKey());
|
||||
});
|
||||
});
|
||||
95
src/algorithms/graph/bridges/graphBridges.js
Normal file
95
src/algorithms/graph/bridges/graphBridges.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,95 @@
|
||||
import depthFirstSearch from '../depth-first-search/depthFirstSearch';
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Helper class for visited vertex metadata.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
class VisitMetadata {
|
||||
constructor({ discoveryTime, lowDiscoveryTime }) {
|
||||
this.discoveryTime = discoveryTime;
|
||||
this.lowDiscoveryTime = lowDiscoveryTime;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @param {Graph} graph
|
||||
* @return {GraphVertex[]}
|
||||
*/
|
||||
export default function graphBridges(graph) {
|
||||
// Set of vertices we've already visited during DFS.
|
||||
const visitedSet = {};
|
||||
|
||||
// Set of bridges.
|
||||
const bridges = {};
|
||||
|
||||
// Time needed to discover to the current vertex.
|
||||
let discoveryTime = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
// Peek the start vertex for DFS traversal.
|
||||
const startVertex = graph.getAllVertices()[0];
|
||||
|
||||
const dfsCallbacks = {
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @param {GraphVertex} currentVertex
|
||||
*/
|
||||
enterVertex: ({ currentVertex }) => {
|
||||
// Tick discovery time.
|
||||
discoveryTime += 1;
|
||||
|
||||
// Put current vertex to visited set.
|
||||
visitedSet[currentVertex.getKey()] = new VisitMetadata({
|
||||
discoveryTime,
|
||||
lowDiscoveryTime: discoveryTime,
|
||||
});
|
||||
},
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @param {GraphVertex} currentVertex
|
||||
* @param {GraphVertex} previousVertex
|
||||
*/
|
||||
leaveVertex: ({ currentVertex, previousVertex }) => {
|
||||
if (previousVertex === null) {
|
||||
// Don't do anything for the root vertex if it is already current (not previous one).
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Check if current node is connected to any early node other then previous one.
|
||||
visitedSet[currentVertex.getKey()].lowDiscoveryTime = currentVertex.getNeighbors()
|
||||
.filter(earlyNeighbor => earlyNeighbor.getKey() !== previousVertex.getKey())
|
||||
.reduce(
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @param {number} lowestDiscoveryTime
|
||||
* @param {GraphVertex} neighbor
|
||||
*/
|
||||
(lowestDiscoveryTime, neighbor) => {
|
||||
const neighborLowTime = visitedSet[neighbor.getKey()].lowDiscoveryTime;
|
||||
return neighborLowTime < lowestDiscoveryTime ? neighborLowTime : lowestDiscoveryTime;
|
||||
},
|
||||
visitedSet[currentVertex.getKey()].lowDiscoveryTime,
|
||||
);
|
||||
|
||||
// Compare low discovery times. In case if current low discovery time is less than the one
|
||||
// in previous vertex then update previous vertex low time.
|
||||
const currentLowDiscoveryTime = visitedSet[currentVertex.getKey()].lowDiscoveryTime;
|
||||
const previousLowDiscoveryTime = visitedSet[previousVertex.getKey()].lowDiscoveryTime;
|
||||
if (currentLowDiscoveryTime < previousLowDiscoveryTime) {
|
||||
visitedSet[previousVertex.getKey()].lowDiscoveryTime = currentLowDiscoveryTime;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Compare current vertex low discovery time with parent discovery time. Check if there
|
||||
// are any short path (back edge) exists. If we can't get to current vertex other then
|
||||
// via parent then the parent vertex is articulation point for current one.
|
||||
const parentDiscoveryTime = visitedSet[previousVertex.getKey()].discoveryTime;
|
||||
if (parentDiscoveryTime < currentLowDiscoveryTime) {
|
||||
const bridge = graph.findEdge(previousVertex, currentVertex);
|
||||
bridges[bridge.getKey()] = bridge;
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
allowTraversal: ({ nextVertex }) => {
|
||||
return !visitedSet[nextVertex.getKey()];
|
||||
},
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// Do Depth First Search traversal over submitted graph.
|
||||
depthFirstSearch(graph, startVertex, dfsCallbacks);
|
||||
|
||||
return Object.values(bridges);
|
||||
}
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user