mirror of
https://github.moeyy.xyz/https://github.com/trekhleb/javascript-algorithms.git
synced 2024-12-25 22:46:20 +08:00
* add japanese translation * fix typo
This commit is contained in:
parent
5c12f45ddc
commit
2632a3a683
95
src/data-structures/doubly-linked-list/README.ja-JP.md
Normal file
95
src/data-structures/doubly-linked-list/README.ja-JP.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,95 @@
|
||||
# 双方向リスト
|
||||
|
||||
コンピュータサイエンスにおいて、**双方向リスト**はノードと呼ばれる一連のリンクレコードからなる連結データ構造です。各ノードはリンクと呼ばれる2つのフィールドを持っていて、これらは一連のノード内における前のノードと次のノードを参照しています。最初のノードの前のリンクと最後のノードの次のリンクはある種の終端を示していて、一般的にはダミーノードやnullが格納され、リストのトラバースを容易に行えるようにしています。もしダミーノードが1つしかない場合、リストはその1つのノードを介して循環的にリンクされます。これは、それぞれ逆の順番の単方向のリンクリストが2つあるものとして考えることができます。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
2つのリンクにより、リストをどちらの方向にもトラバースすることができます。双方向リストはノードの追加や削除の際に、片方向リンクリストと比べてより多くのリンクを変更する必要があります。しかし、その操作は簡単で、より効率的な(最初のノード以外の場合)可能性があります。前のノードのリンクを更新する際に前のノードを保持したり、前のノードを見つけるためにリストをトラバースする必要がありません。
|
||||
|
||||
## 基本操作の擬似コード
|
||||
|
||||
### 挿入
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
Add(value)
|
||||
Pre: value is the value to add to the list
|
||||
Post: value has been placed at the tail of the list
|
||||
n ← node(value)
|
||||
if head = ø
|
||||
head ← n
|
||||
tail ← n
|
||||
else
|
||||
n.previous ← tail
|
||||
tail.next ← n
|
||||
tail ← n
|
||||
end if
|
||||
end Add
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 削除
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
Remove(head, value)
|
||||
Pre: head is the head node in the list
|
||||
value is the value to remove from the list
|
||||
Post: value is removed from the list, true; otherwise false
|
||||
if head = ø
|
||||
return false
|
||||
end if
|
||||
if value = head.value
|
||||
if head = tail
|
||||
head ← ø
|
||||
tail ← ø
|
||||
else
|
||||
head ← head.next
|
||||
head.previous ← ø
|
||||
end if
|
||||
return true
|
||||
end if
|
||||
n ← head.next
|
||||
while n = ø and value !== n.value
|
||||
n ← n.next
|
||||
end while
|
||||
if n = tail
|
||||
tail ← tail.previous
|
||||
tail.next ← ø
|
||||
return true
|
||||
else if n = ø
|
||||
n.previous.next ← n.next
|
||||
n.next.previous ← n.previous
|
||||
return true
|
||||
end if
|
||||
return false
|
||||
end Remove
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 逆トラバース
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
ReverseTraversal(tail)
|
||||
Pre: tail is the node of the list to traverse
|
||||
Post: the list has been traversed in reverse order
|
||||
n ← tail
|
||||
while n = ø
|
||||
yield n.value
|
||||
n ← n.previous
|
||||
end while
|
||||
end Reverse Traversal
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 計算量
|
||||
|
||||
## 時間計算量
|
||||
|
||||
| Access | Search | Insertion | Deletion |
|
||||
| :-------: | :-------: | :-------: | :-------: |
|
||||
| O(n) | O(n) | O(1) | O(n) |
|
||||
|
||||
### 空間計算量
|
||||
|
||||
O(n)
|
||||
|
||||
## 参考
|
||||
|
||||
- [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Doubly_linked_list)
|
||||
- [YouTube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JdQeNxWCguQ&t=7s&index=72&list=PLLXdhg_r2hKA7DPDsunoDZ-Z769jWn4R8)
|
||||
@ -2,7 +2,8 @@
|
||||
|
||||
_Read this in other languages:_
|
||||
[_简体中文_](README.zh-CN.md),
|
||||
[_Русский_](README.ru-RU.md)
|
||||
[_Русский_](README.ru-RU.md),
|
||||
[_日本語_](README.ja-JP.md)
|
||||
|
||||
In computer science, a **doubly linked list** is a linked data structure that
|
||||
consists of a set of sequentially linked records called nodes. Each node contains
|
||||
|
||||
16
src/data-structures/hash-table/README.ja-JP.md
Normal file
16
src/data-structures/hash-table/README.ja-JP.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,16 @@
|
||||
# ハッシュテーブル
|
||||
|
||||
コンピュータサイエンスにおいて、**ハッシュテーブル**(ハッシュマップ)は*キーを値にマッピング*できる*連想配列*の機能を持ったデータ構造です。ハッシュテーブルは*ハッシュ関数*を使ってバケットやスロットの配列へのインデックスを計算し、そこから目的の値を見つけることができます。
|
||||
|
||||
理想的には、ハッシュ関数は各キーを一意のバケットに割り当てますが、ほとんどのハッシュテーブルは不完全なハッシュ関数を採用しているため、複数のキーに対して同じインデックスを生成した時にハッシュの衝突が起こります。このような衝突は何らかの方法で対処する必要があります。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
チェイン法によるハッシュの衝突の解決例
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## 参考
|
||||
|
||||
- [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hash_table)
|
||||
- [YouTube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=shs0KM3wKv8&index=4&list=PLLXdhg_r2hKA7DPDsunoDZ-Z769jWn4R8)
|
||||
@ -2,7 +2,8 @@
|
||||
|
||||
_Read this in other languages:_
|
||||
[_简体中文_](README.zh-CN.md),
|
||||
[_Русский_](README.ru-RU.md)
|
||||
[_Русский_](README.ru-RU.md),
|
||||
[_日本語_](README.ja-JP.md)
|
||||
|
||||
In computing, a **hash table** (hash map) is a data
|
||||
structure which implements an *associative array*
|
||||
|
||||
18
src/data-structures/heap/README.ja-JP.md
Normal file
18
src/data-structures/heap/README.ja-JP.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
|
||||
# ヒープ (データ構造)
|
||||
|
||||
コンピュータサイエンスにおいて、*ヒープ*は特殊な木構造のデータ構造で、後述するヒープの特性を持っています。
|
||||
|
||||
*最小ヒープ*では、もし`P`が`C`の親ノードの場合、`P`のキー(値)は`C`のキーより小さい、または等しくなります。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*最大ヒープ*では、`P`のキーは`C`のキーより大きい、もしくは等しくなります。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
ヒープの「トップ」のノードには親ノードが存在せず、ルートノードと呼ばれます。
|
||||
|
||||
## 参考
|
||||
|
||||
- [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heap_(data_structure))
|
||||
- [YouTube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=t0Cq6tVNRBA&index=5&t=0s&list=PLLXdhg_r2hKA7DPDsunoDZ-Z769jWn4R8)
|
||||
@ -2,7 +2,8 @@
|
||||
|
||||
_Read this in other languages:_
|
||||
[_简体中文_](README.zh-CN.md),
|
||||
[_Русский_](README.ru-RU.md)
|
||||
[_Русский_](README.ru-RU.md),
|
||||
[_日本語_](README.ja-JP.md)
|
||||
|
||||
In computer science, a **heap** is a specialized tree-based
|
||||
data structure that satisfies the heap property described
|
||||
|
||||
141
src/data-structures/linked-list/README.ja-JP.md
Normal file
141
src/data-structures/linked-list/README.ja-JP.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,141 @@
|
||||
# リンクリスト
|
||||
|
||||
コンピュータサイエンスにおいて、**リンクリスト**はデータ要素の線形コレクションです。要素の順番はメモリ内の物理的な配置によっては決まりません。代わりに、各要素が次の要素を指しています。リンクリストはノードのグループからなるデータ構造です。最も単純な形式では、各ノードはデータとシーケンス内における次のノードへの参照(つまり、リンク)で構成されています。この構造はイテレーションにおいて任意の位置へ要素を効率的に挿入、削除することを可能にしています。より複雑なリンクリストではリンクをさらに追加することで、任意の要素の参照から要素を効率的に挿入、削除することを可能にしています。リンクリストの欠点はアクセスタイムが線形である(そして、パイプライン処理が難しい)ことです。ランダムアクセスのような高速なアクセスは実現不可能です。配列の方がリンクリストと比較して参照の局所性が優れています。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## 基本操作の擬似コード
|
||||
|
||||
### 挿入
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
Add(value)
|
||||
Pre: value is the value to add to the list
|
||||
Post: value has been placed at the tail of the list
|
||||
n ← node(value)
|
||||
if head = ø
|
||||
head ← n
|
||||
tail ← n
|
||||
else
|
||||
tail.next ← n
|
||||
tail ← n
|
||||
end if
|
||||
end Add
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
Prepend(value)
|
||||
Pre: value is the value to add to the list
|
||||
Post: value has been placed at the head of the list
|
||||
n ← node(value)
|
||||
n.next ← head
|
||||
head ← n
|
||||
if tail = ø
|
||||
tail ← n
|
||||
end
|
||||
end Prepend
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 検索
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
Contains(head, value)
|
||||
Pre: head is the head node in the list
|
||||
value is the value to search for
|
||||
Post: the item is either in the linked list, true; otherwise false
|
||||
n ← head
|
||||
while n != ø and n.value != value
|
||||
n ← n.next
|
||||
end while
|
||||
if n = ø
|
||||
return false
|
||||
end if
|
||||
return true
|
||||
end Contains
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 削除
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
Remove(head, value)
|
||||
Pre: head is the head node in the list
|
||||
value is the value to remove from the list
|
||||
Post: value is removed from the list, true, otherwise false
|
||||
if head = ø
|
||||
return false
|
||||
end if
|
||||
n ← head
|
||||
if n.value = value
|
||||
if head = tail
|
||||
head ← ø
|
||||
tail ← ø
|
||||
else
|
||||
head ← head.next
|
||||
end if
|
||||
return true
|
||||
end if
|
||||
while n.next != ø and n.next.value != value
|
||||
n ← n.next
|
||||
end while
|
||||
if n.next != ø
|
||||
if n.next = tail
|
||||
tail ← n
|
||||
end if
|
||||
n.next ← n.next.next
|
||||
return true
|
||||
end if
|
||||
return false
|
||||
end Remove
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### トラバース
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
Traverse(head)
|
||||
Pre: head is the head node in the list
|
||||
Post: the items in the list have been traversed
|
||||
n ← head
|
||||
while n != ø
|
||||
yield n.value
|
||||
n ← n.next
|
||||
end while
|
||||
end Traverse
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 逆トラバース
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
ReverseTraversal(head, tail)
|
||||
Pre: head and tail belong to the same list
|
||||
Post: the items in the list have been traversed in reverse order
|
||||
if tail != ø
|
||||
curr ← tail
|
||||
while curr != head
|
||||
prev ← head
|
||||
while prev.next != curr
|
||||
prev ← prev.next
|
||||
end while
|
||||
yield curr.value
|
||||
curr ← prev
|
||||
end while
|
||||
yield curr.value
|
||||
end if
|
||||
end ReverseTraversal
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 計算量
|
||||
|
||||
### 時間計算量
|
||||
|
||||
| Access | Search | Insertion | Deletion |
|
||||
| :-------: | :-------: | :-------: | :-------: |
|
||||
| O(n) | O(n) | O(1) | O(n) |
|
||||
|
||||
### 空間計算量
|
||||
|
||||
O(n)
|
||||
|
||||
## 参考
|
||||
|
||||
- [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linked_list)
|
||||
- [YouTube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=njTh_OwMljA&index=2&t=1s&list=PLLXdhg_r2hKA7DPDsunoDZ-Z769jWn4R8)
|
||||
@ -3,7 +3,8 @@
|
||||
_Read this in other languages:_
|
||||
[_简体中文_](README.zh-CN.md),
|
||||
[_Русский_](README.ru-RU.md),
|
||||
[_Português_](README.pt-BR.md)
|
||||
[_Português_](README.pt-BR.md),
|
||||
[_日本語_](README.ja-JP.md)
|
||||
|
||||
In computer science, a **linked list** is a linear collection
|
||||
of data elements, in which linear order is not given by
|
||||
|
||||
10
src/data-structures/priority-queue/README.ja-JP.md
Normal file
10
src/data-structures/priority-queue/README.ja-JP.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,10 @@
|
||||
# 優先度付きキュー
|
||||
|
||||
コンピュータサイエンスにおいて、**優先度付きキュー**は通常のキューやスタックのデータ構造と似た抽象データ型ですが、各要素に「優先度」が関連づけられています。優先度付きキューでは優先度の高い要素が優先度の低い要素よりも先に処理されます。もし2つの要素が同じ優先度だった場合、それらはキュー内の順序に従って処理されます。
|
||||
|
||||
優先度付きキューは多くの場合ヒープによって実装されていますが、概念的にはヒープとは異なります。優先度付きキューは「リスト」や「マップ」のような抽象的な概念です。リストがリンクリストや配列で実装できるのと同様に、優先度付きキューはヒープや未ソート配列のような様々な方法で実装することができます。
|
||||
|
||||
## 参考
|
||||
|
||||
- [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Priority_queue)
|
||||
- [YouTube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wptevk0bshY&list=PLLXdhg_r2hKA7DPDsunoDZ-Z769jWn4R8&index=6)
|
||||
@ -2,7 +2,8 @@
|
||||
|
||||
_Read this in other languages:_
|
||||
[_简体中文_](README.zh-CN.md),
|
||||
[_Русский_](README.ru-RU.md)
|
||||
[_Русский_](README.ru-RU.md),
|
||||
[_日本語_](README.ja-JP.md)
|
||||
|
||||
In computer science, a **priority queue** is an abstract data type
|
||||
which is like a regular queue or stack data structure, but where
|
||||
|
||||
12
src/data-structures/queue/README.ja-JP.md
Normal file
12
src/data-structures/queue/README.ja-JP.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,12 @@
|
||||
# キュー
|
||||
|
||||
コンピュータサイエンスにおいて、**キュー**は特定の種類の抽象データ型またはコレクションです。コレクションの中のエンティティは順番に並べられており、コレクションに対する基本的な(または唯一の)操作は末尾にエンティティを追加するエンキューと、先頭からエンティティを削除するデキューがあります。これにより、キューは先入れ先出し(FIFO)のデータ構造となります。FIFOのデータ構造では、キューに追加された最初の要素が最初に削除されます。これは、新しい要素が追加されたら、その要素を削除するにはそれまでに追加された全ての要素が削除されなければならないという要件と同じです。多くの場合、ピークのような先頭の要素を検査する操作も備えていて、これはデキューせずに先頭の要素の値を返します。キューは線形のデータ構造や、より抽象的なシーケンシャルなコレクションの一例です。
|
||||
|
||||
FIFO(先入れ先出し)のキュー
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## 参考
|
||||
|
||||
- [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Queue_(abstract_data_type))
|
||||
- [YouTube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wjI1WNcIntg&list=PLLXdhg_r2hKA7DPDsunoDZ-Z769jWn4R8&index=3&)
|
||||
@ -2,7 +2,8 @@
|
||||
|
||||
_Read this in other languages:_
|
||||
[_简体中文_](README.zh-CN.md),
|
||||
[_Русский_](README.ru-RU.md)
|
||||
[_Русский_](README.ru-RU.md),
|
||||
[_日本語_](README.ja-JP.md)
|
||||
|
||||
In computer science, a **queue** is a particular kind of abstract data
|
||||
type or collection in which the entities in the collection are
|
||||
|
||||
17
src/data-structures/stack/README.ja-JP.md
Normal file
17
src/data-structures/stack/README.ja-JP.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
|
||||
# スタック
|
||||
|
||||
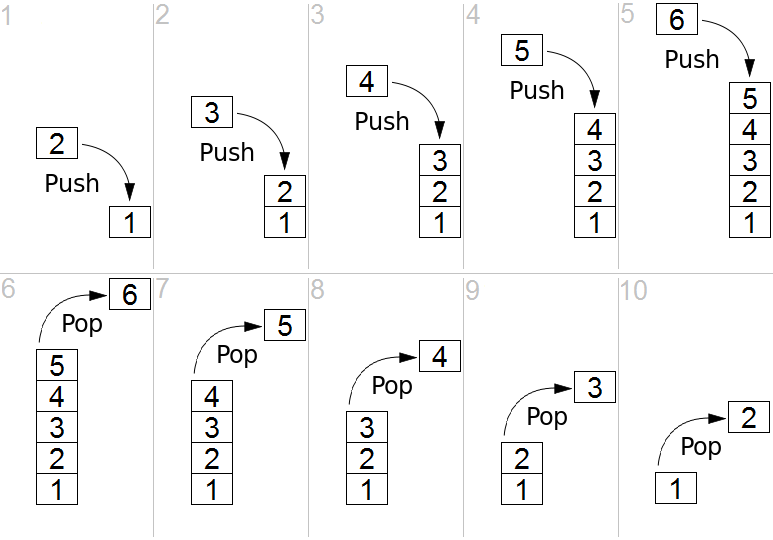
コンピュータサイエンスにおいて、**スタック**は抽象データ型で、2つの主要な操作ができる要素のコレクションです。
|
||||
|
||||
* **プッシュ**はコレクションに要素を追加します。
|
||||
* **ポップ**は最近追加された要素でまだ削除されていないものを削除します。
|
||||
|
||||
要素がスタックから外れる順番から、LIFO(後入れ先出し)とも呼ばれます。スタックに変更を加えることなく、先頭の要素を検査するピーク操作を備えることもあります。「スタック」という名前は、物理的な物を上に積み重ねていく様子との類似性に由来しています。一番上の物を取ることは簡単ですが、スタックの下の方にあるものを取るときは先に上にある複数の物を取り除く必要があります。
|
||||
|
||||
プッシュとポップの例
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 参考
|
||||
|
||||
- [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stack_(abstract_data_type))
|
||||
- [YouTube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wjI1WNcIntg&list=PLLXdhg_r2hKA7DPDsunoDZ-Z769jWn4R8&index=3&)
|
||||
@ -2,7 +2,8 @@
|
||||
|
||||
_Read this in other languages:_
|
||||
[_简体中文_](README.zh-CN.md),
|
||||
[_Русский_](README.ru-RU.md)
|
||||
[_Русский_](README.ru-RU.md),
|
||||
[_日本語_](README.ja-JP.md)
|
||||
|
||||
In computer science, a **stack** is an abstract data type that serves
|
||||
as a collection of elements, with two principal operations:
|
||||
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user