mirror of
https://github.moeyy.xyz/https://github.com/trekhleb/javascript-algorithms.git
synced 2024-11-14 23:12:58 +08:00
Merge branch 'master' into patch-1
This commit is contained in:
commit
53ea385bd0
@ -3,8 +3,11 @@ dist: trusty
|
||||
language: node_js
|
||||
node_js:
|
||||
- node
|
||||
install:
|
||||
- npm install -g codecov
|
||||
- npm install
|
||||
script:
|
||||
- npm run ci
|
||||
- npm run codecov
|
||||
- codecov
|
||||
notifications:
|
||||
email: false
|
||||
|
||||
@ -22,21 +22,21 @@ _Read this in other languages:_
|
||||
|
||||
`B` - 初学者, `A` - 进阶
|
||||
|
||||
* `B` [链表](src/data-structures/linked-list)
|
||||
* `B` [双向链表](src/data-structures/doubly-linked-list)
|
||||
* `B` [队列](src/data-structures/queue)
|
||||
* `B` [栈](src/data-structures/stack)
|
||||
* `B` [哈希表](src/data-structures/hash-table)
|
||||
* `B` [堆](src/data-structures/heap)
|
||||
* `B` [优先队列](src/data-structures/priority-queue)
|
||||
* `B` [链表](src/data-structures/linked-list/README.zh-CN.md)
|
||||
* `B` [双向链表](src/data-structures/doubly-linked-list/README.zh-CN.md)
|
||||
* `B` [队列](src/data-structures/queue/README.zh-CN.md)
|
||||
* `B` [栈](src/data-structures/stack/README.zh-CN.md)
|
||||
* `B` [哈希表](src/data-structures/hash-table/README.zh-CN.md)
|
||||
* `B` [堆](src/data-structures/heap/README.zh-CN.md)
|
||||
* `B` [优先队列](src/data-structures/priority-queue/README.zh-CN.md)
|
||||
* `A` [字典树](src/data-structures/trie)
|
||||
* `A` [树](src/data-structures/tree)
|
||||
* `A` [树](src/data-structures/tree/README.zh-CN.md)
|
||||
* `A` [二叉查找树](src/data-structures/tree/binary-search-tree)
|
||||
* `A` [AVL 树](src/data-structures/tree/avl-tree)
|
||||
* `A` [红黑树](src/data-structures/tree/red-black-tree)
|
||||
* `A` [线段树](src/data-structures/tree/segment-tree) - 使用 最小/最大/总和 范围查询示例
|
||||
* `A` [树状数组](src/data-structures/tree/fenwick-tree) (二叉索引树)
|
||||
* `A` [图](src/data-structures/graph) (有向图与无向图)
|
||||
* `A` [图](src/data-structures/graph/README.zh-CN.md) (有向图与无向图)
|
||||
* `A` [并查集](src/data-structures/disjoint-set)
|
||||
* `A` [布隆过滤器](src/data-structures/bloom-filter)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
23
package-lock.json
generated
23
package-lock.json
generated
@ -181,12 +181,6 @@
|
||||
"sprintf-js": "~1.0.2"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"argv": {
|
||||
"version": "0.0.2",
|
||||
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/argv/-/argv-0.0.2.tgz",
|
||||
"integrity": "sha1-7L0W+JSbFXGDcRsb2jNPN4QBhas=",
|
||||
"dev": true
|
||||
},
|
||||
"aria-query": {
|
||||
"version": "3.0.0",
|
||||
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/aria-query/-/aria-query-3.0.0.tgz",
|
||||
@ -1435,17 +1429,6 @@
|
||||
"integrity": "sha1-DQcLTQQ6W+ozovGkDi7bPZpMz3c=",
|
||||
"dev": true
|
||||
},
|
||||
"codecov": {
|
||||
"version": "3.0.2",
|
||||
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/codecov/-/codecov-3.0.2.tgz",
|
||||
"integrity": "sha512-9ljtIROIjPIUmMRqO+XuDITDoV8xRrZmA0jcEq6p2hg2+wY9wGmLfreAZGIL72IzUfdEDZaU8+Vjidg1fBQ8GQ==",
|
||||
"dev": true,
|
||||
"requires": {
|
||||
"argv": "0.0.2",
|
||||
"request": "^2.81.0",
|
||||
"urlgrey": "0.4.4"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"collection-visit": {
|
||||
"version": "1.0.0",
|
||||
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/collection-visit/-/collection-visit-1.0.0.tgz",
|
||||
@ -9037,12 +9020,6 @@
|
||||
"integrity": "sha1-2pN/emLiH+wf0Y1Js1wpNQZ6bHI=",
|
||||
"dev": true
|
||||
},
|
||||
"urlgrey": {
|
||||
"version": "0.4.4",
|
||||
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/urlgrey/-/urlgrey-0.4.4.tgz",
|
||||
"integrity": "sha1-iS/pWWCAXoVRnxzUOJ8stMu3ZS8=",
|
||||
"dev": true
|
||||
},
|
||||
"use": {
|
||||
"version": "3.1.0",
|
||||
"resolved": "https://registry.npmjs.org/use/-/use-3.1.0.tgz",
|
||||
|
||||
@ -6,8 +6,7 @@
|
||||
"scripts": {
|
||||
"lint": "eslint ./src/*",
|
||||
"test": "jest",
|
||||
"ci": "npm run lint && npm run test -- --coverage",
|
||||
"codecov": "codecov"
|
||||
"ci": "npm run lint && npm run test -- --coverage"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"pre-commit": [
|
||||
"lint",
|
||||
@ -27,7 +26,9 @@
|
||||
"javascript-algorithms",
|
||||
"sorting-algorithms",
|
||||
"graph",
|
||||
"tree"
|
||||
"tree",
|
||||
"interview",
|
||||
"interview-preparation"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"author": "Oleksii Trekhleb (https://www.linkedin.com/in/trekhleb/)",
|
||||
"license": "MIT",
|
||||
@ -39,7 +40,6 @@
|
||||
"@types/jest": "^23.1.4",
|
||||
"babel-cli": "^6.26.0",
|
||||
"babel-preset-env": "^1.7.0",
|
||||
"codecov": "^3.0.2",
|
||||
"eslint": "^4.19.1",
|
||||
"eslint-config-airbnb": "^17.0.0",
|
||||
"eslint-plugin-import": "^2.13.0",
|
||||
|
||||
@ -3,6 +3,10 @@ import bfMaximumSubarray from '../bfMaximumSubarray';
|
||||
describe('bfMaximumSubarray', () => {
|
||||
it('should find maximum subarray using brute force algorithm', () => {
|
||||
expect(bfMaximumSubarray([])).toEqual([]);
|
||||
expect(bfMaximumSubarray([0, 0])).toEqual([0]);
|
||||
expect(bfMaximumSubarray([0, 0, 1])).toEqual([0, 0, 1]);
|
||||
expect(bfMaximumSubarray([0, 0, 1, 2])).toEqual([0, 0, 1, 2]);
|
||||
expect(bfMaximumSubarray([0, 0, -1, 2])).toEqual([2]);
|
||||
expect(bfMaximumSubarray([-1, -2, -3, -4, -5])).toEqual([-1]);
|
||||
expect(bfMaximumSubarray([1, 2, 3, 2, 3, 4, 5])).toEqual([1, 2, 3, 2, 3, 4, 5]);
|
||||
expect(bfMaximumSubarray([-2, 1, -3, 4, -1, 2, 1, -5, 4])).toEqual([4, -1, 2, 1]);
|
||||
|
||||
@ -3,6 +3,10 @@ import dpMaximumSubarray from '../dpMaximumSubarray';
|
||||
describe('dpMaximumSubarray', () => {
|
||||
it('should find maximum subarray using dynamic programming algorithm', () => {
|
||||
expect(dpMaximumSubarray([])).toEqual([]);
|
||||
expect(dpMaximumSubarray([0, 0])).toEqual([0]);
|
||||
expect(dpMaximumSubarray([0, 0, 1])).toEqual([0, 0, 1]);
|
||||
expect(dpMaximumSubarray([0, 0, 1, 2])).toEqual([0, 0, 1, 2]);
|
||||
expect(dpMaximumSubarray([0, 0, -1, 2])).toEqual([2]);
|
||||
expect(dpMaximumSubarray([-1, -2, -3, -4, -5])).toEqual([-1]);
|
||||
expect(dpMaximumSubarray([1, 2, 3, 2, 3, 4, 5])).toEqual([1, 2, 3, 2, 3, 4, 5]);
|
||||
expect(dpMaximumSubarray([-2, 1, -3, 4, -1, 2, 1, -5, 4])).toEqual([4, -1, 2, 1]);
|
||||
|
||||
@ -6,57 +6,40 @@
|
||||
* @return {Number[]}
|
||||
*/
|
||||
export default function dpMaximumSubarray(inputArray) {
|
||||
// Check if all elements of inputArray are negative ones and return the highest
|
||||
// one in this case.
|
||||
let allNegative = true;
|
||||
let highestElementValue = null;
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < inputArray.length; i += 1) {
|
||||
if (inputArray[i] >= 0) {
|
||||
allNegative = false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
// We iterate through the inputArray once, using a greedy approach to keep track of the maximum
|
||||
// sum we've seen so far and the current sum.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The currentSum variable gets reset to 0 every time it drops below 0.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The maxSum variable is set to -Infinity so that if all numbers are negative, the highest
|
||||
// negative number will constitute the maximum subarray.
|
||||
|
||||
if (highestElementValue === null || highestElementValue < inputArray[i]) {
|
||||
highestElementValue = inputArray[i];
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (allNegative && highestElementValue !== null) {
|
||||
return [highestElementValue];
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Let's assume that there is at list one positive integer exists in array.
|
||||
// And thus the maximum sum will for sure be grater then 0. Thus we're able
|
||||
// to always reset max sum to zero.
|
||||
let maxSum = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
// This array will keep a combination that gave the highest sum.
|
||||
let maxSubArray = [];
|
||||
|
||||
// Current sum and subarray that will memoize all previous computations.
|
||||
let maxSum = -Infinity;
|
||||
let currentSum = 0;
|
||||
let currentSubArray = [];
|
||||
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < inputArray.length; i += 1) {
|
||||
// Let's add current element value to the current sum.
|
||||
currentSum += inputArray[i];
|
||||
// We need to keep track of the starting and ending indices that contributed to our maxSum
|
||||
// so that we can return the actual subarray. From the beginning let's assume that whole array
|
||||
// is contributing to maxSum.
|
||||
let maxStartIndex = 0;
|
||||
let maxEndIndex = inputArray.length - 1;
|
||||
let currentStartIndex = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
if (currentSum < 0) {
|
||||
// If the sum went below zero then reset it and don't add current element to max subarray.
|
||||
currentSum = 0;
|
||||
// Reset current subarray.
|
||||
currentSubArray = [];
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// If current sum stays positive then add current element to current sub array.
|
||||
currentSubArray.push(inputArray[i]);
|
||||
inputArray.forEach((currentNumber, currentIndex) => {
|
||||
currentSum += currentNumber;
|
||||
|
||||
if (currentSum > maxSum) {
|
||||
// If current sum became greater then max registered sum then update
|
||||
// max sum and max subarray.
|
||||
maxSum = currentSum;
|
||||
maxSubArray = currentSubArray.slice();
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Update maxSum and the corresponding indices if we have found a new max.
|
||||
if (maxSum < currentSum) {
|
||||
maxSum = currentSum;
|
||||
maxStartIndex = currentStartIndex;
|
||||
maxEndIndex = currentIndex;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return maxSubArray;
|
||||
// Reset currentSum and currentStartIndex if currentSum drops below 0.
|
||||
if (currentSum < 0) {
|
||||
currentSum = 0;
|
||||
currentStartIndex = currentIndex + 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
return inputArray.slice(maxStartIndex, maxEndIndex + 1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -37,6 +37,8 @@ After this step, the array should look like this
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
> UPD: On the picture below there is a typo and result array is supposed to be `[14, 10, 27, 19, 35, 33, 42, 44]`.
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, we sort the rest of the array using interval of value 1.
|
||||
Shell sort uses insertion sort to sort the array.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -50,5 +52,6 @@ Shell sort uses insertion sort to sort the array.
|
||||
|
||||
## References
|
||||
|
||||
* [Tutorials Point](https://www.tutorialspoint.com/data_structures_algorithms/shell_sort_algorithm.htm)
|
||||
* [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Shellsort)
|
||||
- [Tutorials Point](https://www.tutorialspoint.com/data_structures_algorithms/shell_sort_algorithm.htm)
|
||||
- [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Shellsort)
|
||||
- [YouTube by Rob Edwards](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ddeLSDsYVp8&index=79&list=PLLXdhg_r2hKA7DPDsunoDZ-Z769jWn4R8)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -7,5 +7,16 @@ describe('longestCommonSubstring', () => {
|
||||
expect(longestCommonSubstring('', 'ABC')).toBe('');
|
||||
expect(longestCommonSubstring('ABABC', 'BABCA')).toBe('BABC');
|
||||
expect(longestCommonSubstring('BABCA', 'ABCBA')).toBe('ABC');
|
||||
expect(longestCommonSubstring(
|
||||
'Algorithms and data structures implemented in JavaScript',
|
||||
'Here you may find Algorithms and data structures that are implemented in JavaScript',
|
||||
)).toBe('Algorithms and data structures ');
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
it('should handle unicode correctly', () => {
|
||||
expect(longestCommonSubstring('𐌵𐌵**ABC', '𐌵𐌵--ABC')).toBe('ABC');
|
||||
expect(longestCommonSubstring('𐌵𐌵**A', '𐌵𐌵--A')).toBe('𐌵𐌵');
|
||||
expect(longestCommonSubstring('A买B时', '买B时GD')).toBe('买B时');
|
||||
expect(longestCommonSubstring('After test买时 case', 'another_test买时')).toBe('test买时');
|
||||
});
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,9 +1,16 @@
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @param {string} s1
|
||||
* @param {string} s2
|
||||
* @param {string} string1
|
||||
* @param {string} string2
|
||||
* @return {string}
|
||||
*/
|
||||
export default function longestCommonSubstring(s1, s2) {
|
||||
export default function longestCommonSubstring(string1, string2) {
|
||||
// Convert strings to arrays to treat unicode symbols length correctly.
|
||||
// For example:
|
||||
// '𐌵'.length === 2
|
||||
// [...'𐌵'].length === 1
|
||||
const s1 = [...string1];
|
||||
const s2 = [...string2];
|
||||
|
||||
// Init the matrix of all substring lengths to use Dynamic Programming approach.
|
||||
const substringMatrix = Array(s2.length + 1).fill(null).map(() => {
|
||||
return Array(s1.length + 1).fill(null);
|
||||
|
||||
99
src/data-structures/doubly-linked-list/README.zh-CN.md
Normal file
99
src/data-structures/doubly-linked-list/README.zh-CN.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,99 @@
|
||||
# 双向链表
|
||||
|
||||
在计算机科学中, 一个 **双向链表(doubly linked list)** 是由一组称为节点的顺序链接记录组成的链接数据结构。每个节点包含两个字段,称为链接,它们是对节点序列中上一个节点和下一个节点的引用。开始节点和结束节点的上一个链接和下一个链接分别指向某种终止节点,通常是前哨节点或null,以方便遍历列表。如果只有一个前哨节点,则列表通过前哨节点循环链接。它可以被概念化为两个由相同数据项组成的单链表,但顺序相反。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
两个节点链接允许在任一方向上遍历列表。
|
||||
|
||||
在双向链表中进行添加或者删除节点时,需做的链接更改要比单向链表复杂得多。这种操作在单向链表中更简单高效,因为不需要关注一个节点(除第一个和最后一个节点以外的节点)的两个链接,而只需要关注一个链接即可。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 基础操作的伪代码
|
||||
|
||||
### 插入
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
Add(value)
|
||||
Pre: value is the value to add to the list
|
||||
Post: value has been placed at the tail of the list
|
||||
n ← node(value)
|
||||
if head = ø
|
||||
head ← n
|
||||
tail ← n
|
||||
else
|
||||
n.previous ← tail
|
||||
tail.next ← n
|
||||
tail ← n
|
||||
end if
|
||||
end Add
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 删除
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
Remove(head, value)
|
||||
Pre: head is the head node in the list
|
||||
value is the value to remove from the list
|
||||
Post: value is removed from the list, true; otherwise false
|
||||
if head = ø
|
||||
return false
|
||||
end if
|
||||
if value = head.value
|
||||
if head = tail
|
||||
head ← ø
|
||||
tail ← ø
|
||||
else
|
||||
head ← head.Next
|
||||
head.previous ← ø
|
||||
end if
|
||||
return true
|
||||
end if
|
||||
n ← head.next
|
||||
while n = ø and value = n.value
|
||||
n ← n.next
|
||||
end while
|
||||
if n = tail
|
||||
tail ← tail.previous
|
||||
tail.next ← ø
|
||||
return true
|
||||
else if n = ø
|
||||
n.previous.next ← n.next
|
||||
n.next.previous ← n.previous
|
||||
return true
|
||||
end if
|
||||
return false
|
||||
end Remove
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 反向遍历
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
ReverseTraversal(tail)
|
||||
Pre: tail is the node of the list to traverse
|
||||
Post: the list has been traversed in reverse order
|
||||
n ← tail
|
||||
while n = ø
|
||||
yield n.value
|
||||
n ← n.previous
|
||||
end while
|
||||
end Reverse Traversal
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 复杂度
|
||||
|
||||
## 时间复杂度
|
||||
|
||||
| Access | Search | Insertion | Deletion |
|
||||
| :-------: | :-------: | :-------: | :-------: |
|
||||
| O(n) | O(n) | O(1) | O(1) |
|
||||
|
||||
### 空间复杂度
|
||||
|
||||
O(n)
|
||||
|
||||
## 参考
|
||||
|
||||
- [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Doubly_linked_list)
|
||||
- [YouTube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JdQeNxWCguQ&t=7s&index=72&list=PLLXdhg_r2hKA7DPDsunoDZ-Z769jWn4R8)
|
||||
22
src/data-structures/graph/README.zh-CN.md
Normal file
22
src/data-structures/graph/README.zh-CN.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,22 @@
|
||||
# 图
|
||||
|
||||
在计算机科学中, **图(graph)** 是一种抽象数据类型,
|
||||
旨在实现数学中的无向图和有向图概念,特别是图论领域。
|
||||
|
||||
一个图数据结构是一个(由有限个或者可变数量的)顶点/节点/点和边构成的有限集。
|
||||
|
||||
如果顶点对之间是无序的,称为无序图,否则称为有序图;
|
||||
|
||||
如果顶点对之间的边是没有方向的,称为无向图,否则称为有向图;
|
||||
|
||||
如果顶点对之间的边是有权重的,该图可称为加权图。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## 参考
|
||||
|
||||
- [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Graph_(abstract_data_type))
|
||||
- [Introduction to Graphs on YouTube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gXgEDyodOJU&index=9&list=PLLXdhg_r2hKA7DPDsunoDZ-Z769jWn4R8)
|
||||
- [Graphs representation on YouTube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=k1wraWzqtvQ&index=10&list=PLLXdhg_r2hKA7DPDsunoDZ-Z769jWn4R8)
|
||||
21
src/data-structures/hash-table/README.zh-CN.md
Normal file
21
src/data-structures/hash-table/README.zh-CN.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
|
||||
# 哈希表
|
||||
|
||||
在计算中, 一个 **哈希表(hash table 或hash map)** 是一种实现 *关联数组(associative array)*
|
||||
的抽象数据;类型, 该结构可以将 *键映射到值*。
|
||||
|
||||
哈希表使用 *哈希函数/散列函数* 来计算一个值在数组或桶(buckets)中或槽(slots)中对应的索引,可使用该索引找到所需的值。
|
||||
|
||||
理想情况下,散列函数将为每个键分配给一个唯一的桶(bucket),但是大多数哈希表设计采用不完美的散列函数,这可能会导致"哈希冲突(hash collisions)",也就是散列函数为多个键(key)生成了相同的索引,这种碰撞必须
|
||||
以某种方式进行处理。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
通过单独的链接解决哈希冲突
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## 参考
|
||||
|
||||
- [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hash_table)
|
||||
- [YouTube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=shs0KM3wKv8&index=4&list=PLLXdhg_r2hKA7DPDsunoDZ-Z769jWn4R8)
|
||||
@ -144,18 +144,17 @@ export default class Heap {
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @param {*} item
|
||||
* @param {Comparator} [customFindingComparator]
|
||||
* @param {Comparator} [comparator]
|
||||
* @return {Heap}
|
||||
*/
|
||||
remove(item, customFindingComparator) {
|
||||
remove(item, comparator = this.compare) {
|
||||
// Find number of items to remove.
|
||||
const customComparator = customFindingComparator || this.compare;
|
||||
const numberOfItemsToRemove = this.find(item, customComparator).length;
|
||||
const numberOfItemsToRemove = this.find(item, comparator).length;
|
||||
|
||||
for (let iteration = 0; iteration < numberOfItemsToRemove; iteration += 1) {
|
||||
// We need to find item index to remove each time after removal since
|
||||
// indices are being change after each heapify process.
|
||||
const indexToRemove = this.find(item, customComparator).pop();
|
||||
// indices are being changed after each heapify process.
|
||||
const indexToRemove = this.find(item, comparator).pop();
|
||||
|
||||
// If we need to remove last child in the heap then just remove it.
|
||||
// There is no need to heapify the heap afterwards.
|
||||
@ -166,15 +165,14 @@ export default class Heap {
|
||||
this.heapContainer[indexToRemove] = this.heapContainer.pop();
|
||||
|
||||
// Get parent.
|
||||
const parentItem = this.hasParent(indexToRemove) ? this.parent(indexToRemove) : null;
|
||||
const leftChild = this.hasLeftChild(indexToRemove) ? this.leftChild(indexToRemove) : null;
|
||||
const parentItem = this.parent(indexToRemove);
|
||||
|
||||
// If there is no parent or parent is in incorrect order with the node
|
||||
// If there is no parent or parent is in correct order with the node
|
||||
// we're going to delete then heapify down. Otherwise heapify up.
|
||||
if (
|
||||
leftChild !== null
|
||||
this.hasLeftChild(indexToRemove)
|
||||
&& (
|
||||
parentItem === null
|
||||
!parentItem
|
||||
|| this.pairIsInCorrectOrder(parentItem, this.heapContainer[indexToRemove])
|
||||
)
|
||||
) {
|
||||
@ -190,12 +188,11 @@ export default class Heap {
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @param {*} item
|
||||
* @param {Comparator} [customComparator]
|
||||
* @param {Comparator} [comparator]
|
||||
* @return {Number[]}
|
||||
*/
|
||||
find(item, customComparator) {
|
||||
find(item, comparator = this.compare) {
|
||||
const foundItemIndices = [];
|
||||
const comparator = customComparator || this.compare;
|
||||
|
||||
for (let itemIndex = 0; itemIndex < this.heapContainer.length; itemIndex += 1) {
|
||||
if (comparator.equal(item, this.heapContainer[itemIndex])) {
|
||||
@ -224,9 +221,9 @@ export default class Heap {
|
||||
* @param {number} [customStartIndex]
|
||||
*/
|
||||
heapifyUp(customStartIndex) {
|
||||
// Take last element (last in array or the bottom left in a tree) in
|
||||
// a heap container and lift him up until we find the parent element
|
||||
// that is less then the current new one.
|
||||
// Take the last element (last in array or the bottom left in a tree)
|
||||
// in the heap container and lift it up until it is in the correct
|
||||
// order with respect to its parent element.
|
||||
let currentIndex = customStartIndex || this.heapContainer.length - 1;
|
||||
|
||||
while (
|
||||
@ -241,10 +238,11 @@ export default class Heap {
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @param {number} [customStartIndex]
|
||||
*/
|
||||
heapifyDown(customStartIndex) {
|
||||
// Compare the root element to its children and swap root with the smallest
|
||||
// of children. Do the same for next children after swap.
|
||||
let currentIndex = customStartIndex || 0;
|
||||
heapifyDown(customStartIndex = 0) {
|
||||
// Compare the parent element to its children and swap parent with the appropriate
|
||||
// child (smallest child for MinHeap, largest child for MaxHeap).
|
||||
// Do the same for next children after swap.
|
||||
let currentIndex = customStartIndex;
|
||||
let nextIndex = null;
|
||||
|
||||
while (this.hasLeftChild(currentIndex)) {
|
||||
|
||||
19
src/data-structures/heap/README.zh-CN.md
Normal file
19
src/data-structures/heap/README.zh-CN.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,19 @@
|
||||
# 堆 (数据结构)
|
||||
|
||||
在计算机科学中, 一个 ** 堆(heap)** 是一种特殊的基于树的数据结构,它满足下面描述的堆属性。
|
||||
|
||||
在一个 *最小堆(min heap)* 中, 如果 `P` 是 `C` 的一个父级节点, 那么 `P` 的key(或value)应小于或等于 `C` 的对应值.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在一个 *最大堆(max heap)* 中, `P` 的key(或value)大于 `C` 的对应值。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
在堆“顶部”的没有父级节点的节点,被称之为根节点。
|
||||
|
||||
## 参考
|
||||
|
||||
- [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heap_(data_structure))
|
||||
- [YouTube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=t0Cq6tVNRBA&index=5&t=0s&list=PLLXdhg_r2hKA7DPDsunoDZ-Z769jWn4R8)
|
||||
@ -37,7 +37,20 @@ Add(value)
|
||||
end if
|
||||
end Add
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
Prepend(value)
|
||||
Pre: value is the value to add to the list
|
||||
Post: value has been placed at the head of the list
|
||||
n ← node(value)
|
||||
n.next ← head
|
||||
head ← n
|
||||
if tail = ø
|
||||
tail ← n
|
||||
end
|
||||
end Prepend
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Search
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
@ -76,10 +89,10 @@ Remove(head, value)
|
||||
end if
|
||||
return true
|
||||
end if
|
||||
while n.next = ø and n.next.value = value
|
||||
while n.next != ø and n.next.value != value
|
||||
n ← n.next
|
||||
end while
|
||||
if n.next = ø
|
||||
if n.next != ø
|
||||
if n.next = tail
|
||||
tail ← n
|
||||
end if
|
||||
|
||||
134
src/data-structures/linked-list/README.zh-CN.md
Normal file
134
src/data-structures/linked-list/README.zh-CN.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,134 @@
|
||||
# 链表
|
||||
|
||||
在计算机科学中, 一个 **链表** 是数据元素的线性集合, 元素的线性顺序不是由它们在内存中的物理位置给出的。 相反, 每个元素指向下一个元素。它是由一组节点组成的数据结构,这些节点一起,表示序列。
|
||||
|
||||
在最简单的形式下,每个节点由数据和到序列中下一个节点的引用(换句话说,链接)组成。这种结构允许在迭代期间有效地从序列中的任何位置插入或删除元素。
|
||||
|
||||
更复杂的变体添加额外的链接,允许有效地插入或删除任意元素引用。链表的一个缺点是访问时间是线性的(而且难以管道化)。
|
||||
|
||||
更快的访问,如随机访问,是不可行的。与链表相比,数组具有更好的缓存位置。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## 基本操作的伪代码
|
||||
|
||||
### 插入
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
Add(value)
|
||||
Pre: value is the value to add to the list
|
||||
Post: value has been placed at the tail of the list
|
||||
n ← node(value)
|
||||
if head = ø
|
||||
head ← n
|
||||
tail ← n
|
||||
else
|
||||
tail.next ← n
|
||||
tail ← n
|
||||
end if
|
||||
end Add
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 搜索
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
Contains(head, value)
|
||||
Pre: head is the head node in the list
|
||||
value is the value to search for
|
||||
Post: the item is either in the linked list, true; otherwise false
|
||||
n ← head
|
||||
while n != ø and n.value != value
|
||||
n ← n.next
|
||||
end while
|
||||
if n = ø
|
||||
return false
|
||||
end if
|
||||
return true
|
||||
end Contains
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 删除
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
Remove(head, value)
|
||||
Pre: head is the head node in the list
|
||||
value is the value to remove from the list
|
||||
Post: value is removed from the list, true, otherwise false
|
||||
if head = ø
|
||||
return false
|
||||
end if
|
||||
n ← head
|
||||
if n.value = value
|
||||
if head = tail
|
||||
head ← ø
|
||||
tail ← ø
|
||||
else
|
||||
head ← head.next
|
||||
end if
|
||||
return true
|
||||
end if
|
||||
while n.next = ø and n.next.value = value
|
||||
n ← n.next
|
||||
end while
|
||||
if n.next = ø
|
||||
if n.next = tail
|
||||
tail ← n
|
||||
end if
|
||||
n.next ← n.next.next
|
||||
return true
|
||||
end if
|
||||
return false
|
||||
end Remove
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 遍历
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
Traverse(head)
|
||||
Pre: head is the head node in the list
|
||||
Post: the items in the list have been traversed
|
||||
n ← head
|
||||
while n = 0
|
||||
yield n.value
|
||||
n ← n.next
|
||||
end while
|
||||
end Traverse
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 反向遍历
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
ReverseTraversal(head, tail)
|
||||
Pre: head and tail belong to the same list
|
||||
Post: the items in the list have been traversed in reverse order
|
||||
if tail = ø
|
||||
curr ← tail
|
||||
while curr = head
|
||||
prev ← head
|
||||
while prev.next = curr
|
||||
prev ← prev.next
|
||||
end while
|
||||
yield curr.value
|
||||
curr ← prev
|
||||
end while
|
||||
yeild curr.value
|
||||
end if
|
||||
end ReverseTraversal
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 复杂度
|
||||
|
||||
### 时间复杂度
|
||||
|
||||
| Access | Search | Insertion | Deletion |
|
||||
| :-------: | :-------: | :-------: | :-------: |
|
||||
| O(n) | O(n) | O(1) | O(1) |
|
||||
|
||||
### 空间复杂度
|
||||
|
||||
O(n)
|
||||
|
||||
## 参考
|
||||
|
||||
- [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linked_list)
|
||||
- [YouTube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=njTh_OwMljA&index=2&t=1s&list=PLLXdhg_r2hKA7DPDsunoDZ-Z769jWn4R8)
|
||||
@ -16,6 +16,7 @@ describe('LinkedList', () => {
|
||||
linkedList.append(2);
|
||||
|
||||
expect(linkedList.toString()).toBe('1,2');
|
||||
expect(linkedList.tail.next).toBeNull();
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
it('should prepend node to linked list', () => {
|
||||
|
||||
15
src/data-structures/priority-queue/README.zh-CN.md
Normal file
15
src/data-structures/priority-queue/README.zh-CN.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,15 @@
|
||||
# 优先队列
|
||||
|
||||
在计算机科学中, **优先级队列(priority queue)** 是一种抽象数据类型, 它类似于常规的队列或栈, 但每个元素都有与之关联的“优先级”。
|
||||
|
||||
在优先队列中, 低优先级的元素之前前面应该是高优先级的元素。 如果两个元素具有相同的优先级, 则根据它们在队列中的顺序是它们的出现顺序即可。
|
||||
|
||||
优先队列虽通常用堆来实现,但它在概念上与堆不同。优先队列是一个抽象概念,就像“列表”或“图”这样的抽象概念一样;
|
||||
|
||||
正如列表可以用链表或数组实现一样,优先队列可以用堆或各种其他方法实现,例如无序数组。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 参考
|
||||
|
||||
- [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Priority_queue)
|
||||
- [YouTube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wptevk0bshY&list=PLLXdhg_r2hKA7DPDsunoDZ-Z769jWn4R8&index=6)
|
||||
@ -2,10 +2,10 @@ import LinkedList from '../linked-list/LinkedList';
|
||||
|
||||
export default class Queue {
|
||||
constructor() {
|
||||
// We're going to implement Queue based on LinkedList since this
|
||||
// structures a quite similar. Namely they both operates mostly with
|
||||
// with theirs beginning and the end. Compare enqueue/de-queue
|
||||
// operations of the Queue with append/prepend operations of LinkedList.
|
||||
// We're going to implement Queue based on LinkedList since the two
|
||||
// structures are quite similar. Namely, they both operate mostly on
|
||||
// the elements at the beginning and the end. Compare enqueue/dequeue
|
||||
// operations of Queue with append/deleteHead operations of LinkedList.
|
||||
this.linkedList = new LinkedList();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -13,39 +13,36 @@ export default class Queue {
|
||||
* @return {boolean}
|
||||
*/
|
||||
isEmpty() {
|
||||
// The queue is empty in case if its linked list don't have tail.
|
||||
return !this.linkedList.tail;
|
||||
return !this.linkedList.head;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Read the element at the front of the queue without removing it.
|
||||
* @return {*}
|
||||
*/
|
||||
peek() {
|
||||
if (!this.linkedList.head) {
|
||||
// If linked list is empty then there is nothing to peek from.
|
||||
return null;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Just read the value from the end of linked list without deleting it.
|
||||
return this.linkedList.head.value;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Add a new element to the end of the queue (the tail of the linked list).
|
||||
* This element will be processed after all elements ahead of it.
|
||||
* @param {*} value
|
||||
*/
|
||||
enqueue(value) {
|
||||
// Enqueueing means to stand in the line. Therefore let's just add
|
||||
// new value at the beginning of the linked list. It will need to wait
|
||||
// until all previous nodes will be processed.
|
||||
this.linkedList.append(value);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Remove the element at the front of the queue (the head of the linked list).
|
||||
* If the queue is empty, return null.
|
||||
* @return {*}
|
||||
*/
|
||||
dequeue() {
|
||||
// Let's try to delete the last node from linked list (the tail).
|
||||
// If there is no tail in linked list (it is empty) just return null.
|
||||
const removedHead = this.linkedList.deleteHead();
|
||||
return removedHead ? removedHead.value : null;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
15
src/data-structures/queue/README.zh-CN.md
Normal file
15
src/data-structures/queue/README.zh-CN.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,15 @@
|
||||
# 队列
|
||||
|
||||
在计算机科学中, 一个 **队列(queue)** 是一种特殊类型的抽象数据类型或集合。集合中的实体按顺序保存。
|
||||
|
||||
队列基本操作有两种: 向队列的后端位置添加实体,称为入队,并从队列的前端位置移除实体,称为出队。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
队列中元素先进先出 FIFO (first in, first out)的示意
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## 参考
|
||||
|
||||
- [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Queue_(abstract_data_type))
|
||||
- [YouTube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wjI1WNcIntg&list=PLLXdhg_r2hKA7DPDsunoDZ-Z769jWn4R8&index=3&)
|
||||
21
src/data-structures/stack/README.zh-CN.md
Normal file
21
src/data-structures/stack/README.zh-CN.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
|
||||
# 栈
|
||||
|
||||
在计算机科学中, 一个 **栈(stack)** 时一种抽象数据类型,用作表示元素的集合,具有两种主要操作:
|
||||
|
||||
* **push**, 添加元素到栈的顶端(末尾);
|
||||
* **pop**, 移除栈最顶端(末尾)的元素.
|
||||
|
||||
以上两种操作可以简单概括为“后进先出(LIFO = last in, first out)”。
|
||||
|
||||
此外,应有一个 `peek` 操作用于访问栈当前顶端(末尾)的元素。
|
||||
|
||||
"栈"这个名称,可类比于一组物体的堆叠(一摞书,一摞盘子之类的)。
|
||||
|
||||
栈的 push 和 pop 操作的示意
|
||||
|
||||
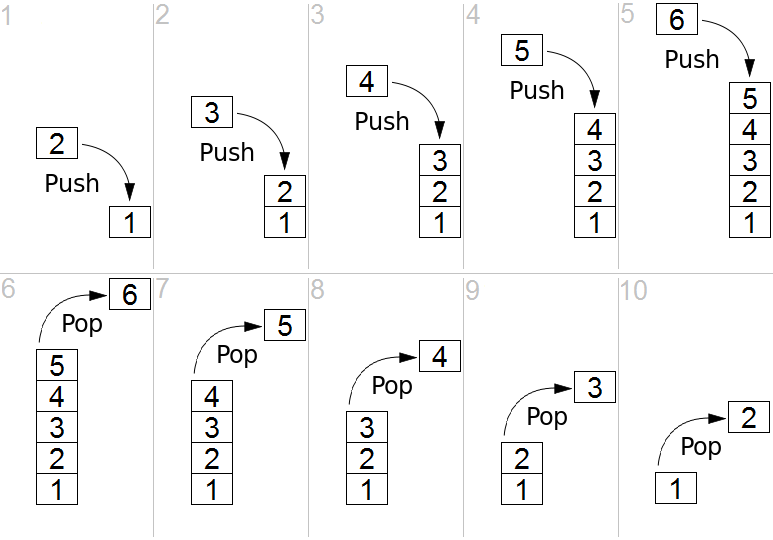
|
||||
|
||||
## 参考
|
||||
|
||||
- [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stack_(abstract_data_type))
|
||||
- [YouTube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wjI1WNcIntg&list=PLLXdhg_r2hKA7DPDsunoDZ-Z769jWn4R8&index=3&)
|
||||
24
src/data-structures/tree/README.zh-CN.md
Normal file
24
src/data-structures/tree/README.zh-CN.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,24 @@
|
||||
# 树
|
||||
|
||||
* [二叉搜索树](binary-search-tree)
|
||||
* [AVL树](avl-tree)
|
||||
* [红黑树](red-black-tree)
|
||||
* [线段树](segment-tree) - with min/max/sum range queries examples
|
||||
* [芬威克树/Fenwick Tree](fenwick-tree) (Binary Indexed Tree)
|
||||
|
||||
在计算机科学中, **树(tree)** 是一种广泛使用的抽象数据类型(ADT)— 或实现此ADT的数据结构 — 模拟分层树结构, 具有根节点和有父节点的子树,表示为一组链接节点。
|
||||
|
||||
树可以被(本地地)递归定义为一个(始于一个根节点的)节点集, 每个节点都是一个包含了值的数据结构, 除了值,还有该节点的节点引用列表(子节点)一起。
|
||||
树的节点之间没有引用重复的约束。
|
||||
|
||||
一棵简单的无序树; 在下图中:
|
||||
|
||||
标记为7的节点具有两个子节点, 标记为2和6;
|
||||
一个父节点,标记为2,作为根节点, 在顶部,没有父节点。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## 参考
|
||||
|
||||
- [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tree_(data_structure))
|
||||
- [YouTube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oSWTXtMglKE&list=PLLXdhg_r2hKA7DPDsunoDZ-Z769jWn4R8&index=8)
|
||||
@ -40,7 +40,7 @@ and geographic information systems.
|
||||
Current implementation of Segment Tree implies that you may
|
||||
pass any binary (with two input params) function to it and
|
||||
thus you're able to do range query for variety of functions.
|
||||
In tests you may fins examples of doing `min`, `max` and `sam` range
|
||||
In tests you may find examples of doing `min`, `max` and `sam` range
|
||||
queries on SegmentTree.
|
||||
|
||||
## References
|
||||
|
||||
16
src/data-structures/trie/README.zh-CN.md
Normal file
16
src/data-structures/trie/README.zh-CN.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,16 @@
|
||||
# 字典树
|
||||
|
||||
在计算机科学中, **字典树(trie,中文又被称为”单词查找树“或 ”键树“)**, 也称为数字树,有时候也被称为基数树或前缀树(因为它们可以通过前缀搜索),它是一种搜索树--一种已排序的数据结构,通常用于存储动态集或键为字符串的关联数组。
|
||||
|
||||
与二叉搜索树不同, 树上没有节点存储与该节点关联的键; 相反,节点在树上的位置定义了与之关联的键。一个节点的全部后代节点都有一个与该节点关联的通用的字符串前缀, 与根节点关联的是空字符串。
|
||||
|
||||
值对于字典树中关联的节点来说,不是必需的,相反,值往往和相关的叶子相关,以及与一些键相关的内部节点相关。
|
||||
|
||||
有关字典树的空间优化示意,请参阅紧凑前缀树
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## 参考
|
||||
|
||||
- [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trie)
|
||||
- [YouTube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zIjfhVPRZCg&list=PLLXdhg_r2hKA7DPDsunoDZ-Z769jWn4R8&index=7&t=0s)
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user