mirror of
https://github.moeyy.xyz/https://github.com/trekhleb/javascript-algorithms.git
synced 2024-12-26 07:01:18 +08:00
Fix typos (#59)
* Fixed typo in the word 'independant' * Fixed typo in the word 'subsequnce' * Fixed typo in the word 'icecream' * Fixed typo in the word 'subsequnce' in shortestCommonSubsequence * Fixed typo in the word 'depected' * Fixed typo in the word 'paramaters'
This commit is contained in:
parent
19aa6fa4fc
commit
5734e0a43e
@ -9,7 +9,7 @@ class VisitMetadata {
|
||||
this.lowDiscoveryTime = lowDiscoveryTime;
|
||||
// We need this in order to check graph root node, whether it has two
|
||||
// disconnected children or not.
|
||||
this.independantChildrenCount = 0;
|
||||
this.independentChildrenCount = 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -49,7 +49,7 @@ export default function articulationPoints(graph) {
|
||||
|
||||
if (previousVertex) {
|
||||
// Update children counter for previous vertex.
|
||||
visitedSet[previousVertex.getKey()].independantChildrenCount += 1;
|
||||
visitedSet[previousVertex.getKey()].independentChildrenCount += 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
/**
|
||||
@ -85,7 +85,7 @@ export default function articulationPoints(graph) {
|
||||
// 2. If its visited time is <= low time of adjacent vertex.
|
||||
if (previousVertex === startVertex) {
|
||||
// Check that root vertex has at least two independent children.
|
||||
if (visitedSet[previousVertex.getKey()].independantChildrenCount >= 2) {
|
||||
if (visitedSet[previousVertex.getKey()].independentChildrenCount >= 2) {
|
||||
articulationPointsSet[previousVertex.getKey()] = previousVertex;
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
|
||||
@ -30,7 +30,7 @@ It is often called "n choose r" (such as "16 choose 3"). And is also known as th
|
||||
|
||||
Repetition is Allowed: such as coins in your pocket `(5,5,5,10,10)`
|
||||
|
||||
Or let us say there are five flavours of icecream:
|
||||
Or let us say there are five flavours of ice cream:
|
||||
`banana`, `chocolate`, `lemon`, `strawberry` and `vanilla`.
|
||||
|
||||
We can have three scoops. How many variations will there be?
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,29 +1,29 @@
|
||||
import longestCommonSubsequnce from '../longestCommonSubsequnce';
|
||||
import longestCommonSubsequence from '../longestCommonSubsequence';
|
||||
|
||||
describe('longestCommonSubsequnce', () => {
|
||||
describe('longestCommonSubsequence', () => {
|
||||
it('should find longest common subsequence for two strings', () => {
|
||||
expect(longestCommonSubsequnce([''], [''])).toEqual(['']);
|
||||
expect(longestCommonSubsequence([''], [''])).toEqual(['']);
|
||||
|
||||
expect(longestCommonSubsequnce([''], ['A', 'B', 'C'])).toEqual(['']);
|
||||
expect(longestCommonSubsequence([''], ['A', 'B', 'C'])).toEqual(['']);
|
||||
|
||||
expect(longestCommonSubsequnce(['A', 'B', 'C'], [''])).toEqual(['']);
|
||||
expect(longestCommonSubsequence(['A', 'B', 'C'], [''])).toEqual(['']);
|
||||
|
||||
expect(longestCommonSubsequnce(
|
||||
expect(longestCommonSubsequence(
|
||||
['A', 'B', 'C'],
|
||||
['D', 'E', 'F', 'G'],
|
||||
)).toEqual(['']);
|
||||
|
||||
expect(longestCommonSubsequnce(
|
||||
expect(longestCommonSubsequence(
|
||||
['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'G', 'H'],
|
||||
['A', 'E', 'D', 'F', 'H', 'R'],
|
||||
)).toEqual(['A', 'D', 'H']);
|
||||
|
||||
expect(longestCommonSubsequnce(
|
||||
expect(longestCommonSubsequence(
|
||||
['A', 'G', 'G', 'T', 'A', 'B'],
|
||||
['G', 'X', 'T', 'X', 'A', 'Y', 'B'],
|
||||
)).toEqual(['G', 'T', 'A', 'B']);
|
||||
|
||||
expect(longestCommonSubsequnce(
|
||||
expect(longestCommonSubsequence(
|
||||
['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'A', 'F'],
|
||||
['A', 'C', 'B', 'C', 'F'],
|
||||
)).toEqual(['A', 'B', 'C', 'F']);
|
||||
@ -3,7 +3,7 @@
|
||||
* @param {string[]} set2
|
||||
* @return {string[]}
|
||||
*/
|
||||
export default function longestCommonSubsequnce(set1, set2) {
|
||||
export default function longestCommonSubsequence(set1, set2) {
|
||||
// Init LCS matrix.
|
||||
const lcsMatrix = Array(set2.length + 1).fill(null).map(() => Array(set1.length + 1).fill(null));
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
||||
import longestCommonSubsequnce from '../longest-common-subsequnce/longestCommonSubsequnce';
|
||||
import longestCommonSubsequence from '../longest-common-subsequence/longestCommonSubsequence';
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @param {string[]} set1
|
||||
@ -8,9 +8,9 @@ import longestCommonSubsequnce from '../longest-common-subsequnce/longestCommonS
|
||||
|
||||
export default function shortestCommonSupersequence(set1, set2) {
|
||||
// Let's first find the longest common subsequence of two sets.
|
||||
const lcs = longestCommonSubsequnce(set1, set2);
|
||||
const lcs = longestCommonSubsequence(set1, set2);
|
||||
|
||||
// If LCS is empty then the shortest common supersequnce would be just
|
||||
// If LCS is empty then the shortest common supersequence would be just
|
||||
// concatenation of two sequences.
|
||||
if (lcs.length === 1 && lcs[0] === '') {
|
||||
return set1.concat(set2);
|
||||
|
||||
@ -32,7 +32,7 @@ element is very small.
|
||||
|
||||
In first step we calculate the count of all the elements of the
|
||||
input array `A`. Then Store the result in the count array `C`.
|
||||
The way we count is depected below.
|
||||
The way we count is depicted below.
|
||||
|
||||
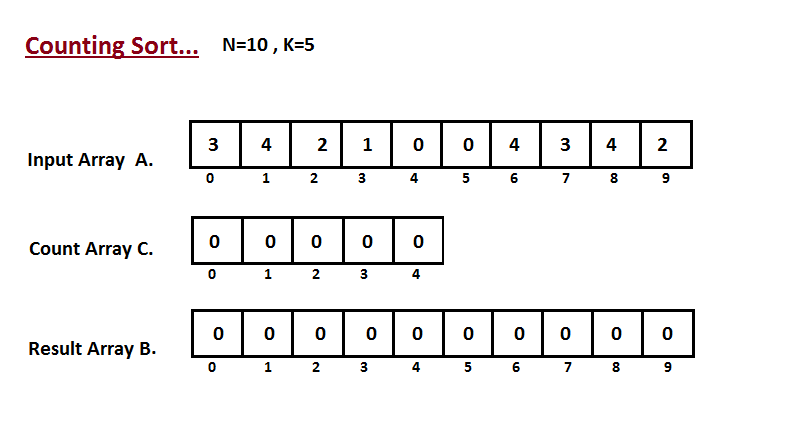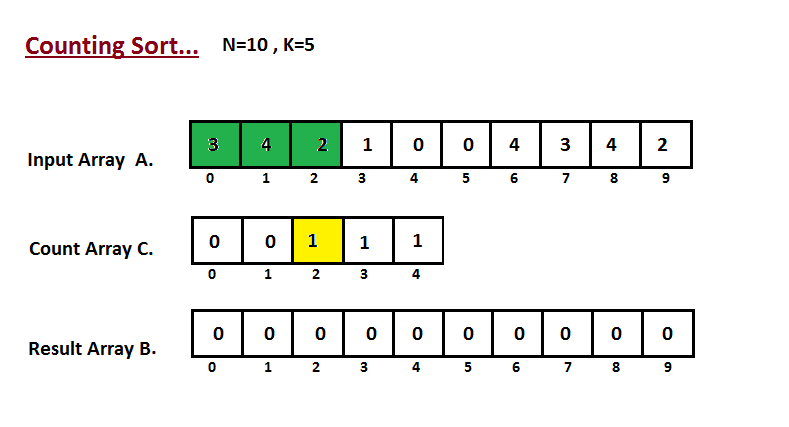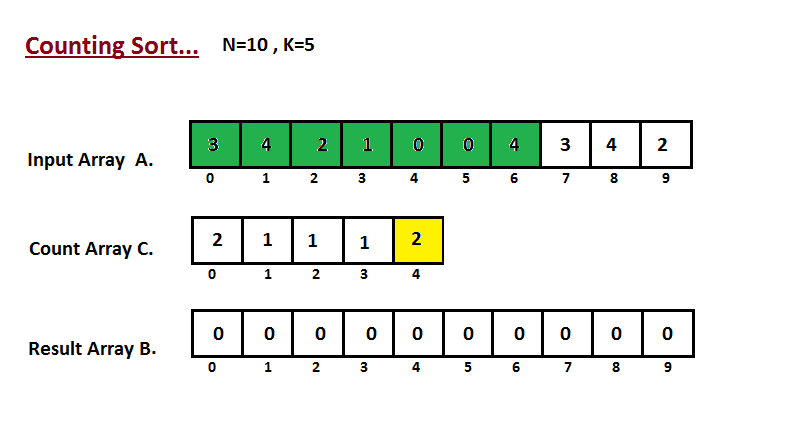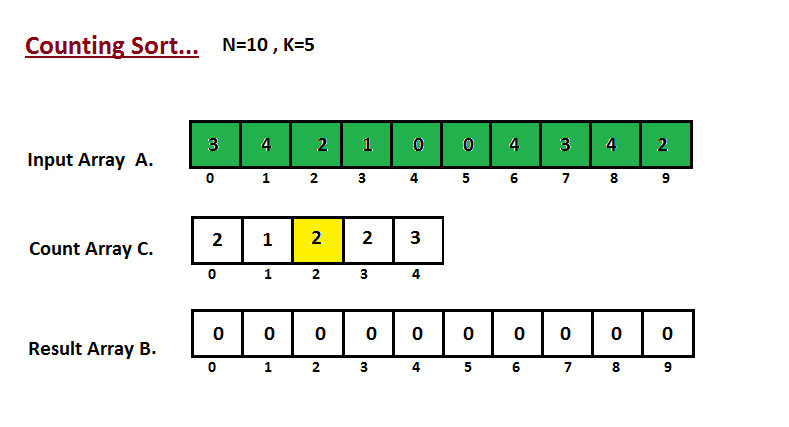
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -54,7 +54,7 @@ export default class QuickSortInPlace extends Sort {
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* While we can use a default parameter to set `low` to 0, we would
|
||||
* still have to set `high`'s default within the function as we
|
||||
* don't have access to `array.length - 1` when declaring paramaters
|
||||
* don't have access to `array.length - 1` when declaring parameters
|
||||
*/
|
||||
const lowIndex = inputLowIndex === undefined ? 0 : inputLowIndex;
|
||||
const highIndex = inputHighIndex === undefined ? array.length - 1 : inputHighIndex;
|
||||
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user