mirror of
https://github.moeyy.xyz/https://github.com/trekhleb/javascript-algorithms.git
synced 2024-11-10 11:09:43 +08:00
Add dijkstra.
This commit is contained in:
parent
119cddc8fc
commit
59f61dc132
@ -65,11 +65,11 @@
|
||||
* **Graph**
|
||||
* [Depth-First Search](https://github.com/trekhleb/javascript-algorithms/tree/master/src/algorithms/graph/depth-first-search) (DFS)
|
||||
* [Breadth-First Search](https://github.com/trekhleb/javascript-algorithms/tree/master/src/algorithms/graph/breadth-first-search) (BFS)
|
||||
* [Dijkstra Algorithm](https://github.com/trekhleb/javascript-algorithms/tree/master/src/algorithms/graph/dijkstra) - finding shortest path
|
||||
* Bellman Ford
|
||||
* Detect Cycle
|
||||
* Topological Sorting
|
||||
* Dijkstra Algorithm to Find Shortest Path
|
||||
* Eulerian path, Eulerian circuit
|
||||
* Bellman Ford
|
||||
* Strongly Connected Component algorithm
|
||||
* Shortest Path Faster Algorithm (SPFA)
|
||||
* **Minimum Spanning Tree**
|
||||
@ -84,6 +84,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
* **Greedy**
|
||||
* [Unbound Knapsack Problem](https://github.com/trekhleb/javascript-algorithms/tree/master/src/algorithms/sets/knapsack-problem)
|
||||
* [Dijkstra Algorithm](https://github.com/trekhleb/javascript-algorithms/tree/master/src/algorithms/graph/dijkstra) - finding shortest path
|
||||
* **Divide and Conquer**
|
||||
* [Euclidean Algorithm](https://github.com/trekhleb/javascript-algorithms/tree/master/src/algorithms/math/euclidean-algorithm) - calculate the Greatest Common Divisor (GCD)
|
||||
* [Permutations](https://github.com/trekhleb/javascript-algorithms/tree/master/src/algorithms/sets/permutations) (with and without repetitions)
|
||||
|
||||
25
src/algorithms/graph/dijkstra/README.md
Normal file
25
src/algorithms/graph/dijkstra/README.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
|
||||
# Dijkstra's Algorithm
|
||||
|
||||
Dijkstra's algorithm is an algorithm for finding the shortest
|
||||
paths between nodes in a graph, which may represent, for example,
|
||||
road networks.
|
||||
|
||||
The algorithm exists in many variants; Dijkstra's original variant
|
||||
found the shortest path between two nodes, but a more common
|
||||
variant fixes a single node as the "source" node and finds
|
||||
shortest paths from the source to all other nodes in the graph,
|
||||
producing a shortest-path tree.
|
||||
|
||||
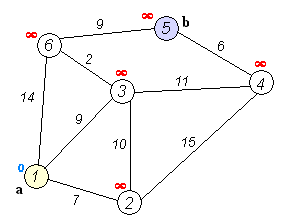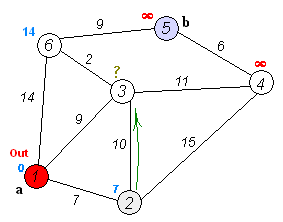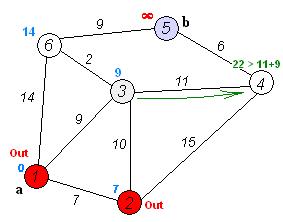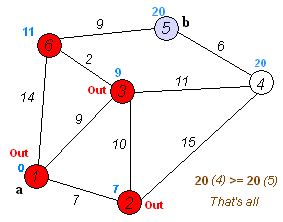
|
||||
|
||||
Dijkstra's algorithm to find the shortest path between `a` and `b`.
|
||||
It picks the unvisited vertex with the lowest distance,
|
||||
calculates the distance through it to each unvisited neighbor,
|
||||
and updates the neighbor's distance if smaller. Mark visited
|
||||
(set to red) when done with neighbors.
|
||||
|
||||
## References
|
||||
|
||||
- [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dijkstra%27s_algorithm)
|
||||
- [On YouTube by Nathaniel Fan](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gdmfOwyQlcI)
|
||||
- [On YouTube by Tushar Roy](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lAXZGERcDf4)
|
||||
59
src/algorithms/graph/dijkstra/__test__/dijkstra.test.js
Normal file
59
src/algorithms/graph/dijkstra/__test__/dijkstra.test.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,59 @@
|
||||
import GraphVertex from '../../../../data-structures/graph/GraphVertex';
|
||||
import GraphEdge from '../../../../data-structures/graph/GraphEdge';
|
||||
import Graph from '../../../../data-structures/graph/Graph';
|
||||
import dijkstra from '../dijkstra';
|
||||
|
||||
describe('dijkstra', () => {
|
||||
it('should find minimum paths to all vertices', () => {
|
||||
const vertexA = new GraphVertex('A');
|
||||
const vertexB = new GraphVertex('B');
|
||||
const vertexC = new GraphVertex('C');
|
||||
const vertexD = new GraphVertex('D');
|
||||
const vertexE = new GraphVertex('E');
|
||||
const vertexF = new GraphVertex('F');
|
||||
const vertexG = new GraphVertex('G');
|
||||
const vertexH = new GraphVertex('H');
|
||||
|
||||
const edgeAB = new GraphEdge(vertexA, vertexB, 4);
|
||||
const edgeAE = new GraphEdge(vertexA, vertexE, 7);
|
||||
const edgeAC = new GraphEdge(vertexA, vertexC, 3);
|
||||
const edgeBC = new GraphEdge(vertexB, vertexC, 6);
|
||||
const edgeBD = new GraphEdge(vertexB, vertexD, 5);
|
||||
const edgeEC = new GraphEdge(vertexE, vertexC, 8);
|
||||
const edgeED = new GraphEdge(vertexE, vertexD, 2);
|
||||
const edgeDC = new GraphEdge(vertexD, vertexC, 11);
|
||||
const edgeDG = new GraphEdge(vertexD, vertexG, 10);
|
||||
const edgeDF = new GraphEdge(vertexD, vertexF, 2);
|
||||
const edgeFG = new GraphEdge(vertexF, vertexG, 3);
|
||||
const edgeEG = new GraphEdge(vertexE, vertexG, 5);
|
||||
|
||||
const graph = new Graph();
|
||||
graph
|
||||
.addVertex(vertexH)
|
||||
.addEdge(edgeAB)
|
||||
.addEdge(edgeAE)
|
||||
.addEdge(edgeAC)
|
||||
.addEdge(edgeBC)
|
||||
.addEdge(edgeBD)
|
||||
.addEdge(edgeEC)
|
||||
.addEdge(edgeED)
|
||||
.addEdge(edgeDC)
|
||||
.addEdge(edgeDG)
|
||||
.addEdge(edgeDF)
|
||||
.addEdge(edgeFG)
|
||||
.addEdge(edgeEG);
|
||||
|
||||
const distances = dijkstra(graph, vertexA);
|
||||
|
||||
expect(distances).toEqual({
|
||||
H: Infinity,
|
||||
A: 0,
|
||||
B: 4,
|
||||
E: 7,
|
||||
C: 3,
|
||||
D: 9,
|
||||
G: 12,
|
||||
F: 11,
|
||||
});
|
||||
});
|
||||
});
|
||||
48
src/algorithms/graph/dijkstra/dijkstra.js
Normal file
48
src/algorithms/graph/dijkstra/dijkstra.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
|
||||
import PriorityQueue from '../../../data-structures/priority-queue/PriorityQueue';
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @param {Graph} graph
|
||||
* @param {GraphVertex} startVertex
|
||||
*/
|
||||
export default function dijkstra(graph, startVertex) {
|
||||
const distances = {};
|
||||
const visitedVertices = {};
|
||||
const queue = new PriorityQueue();
|
||||
|
||||
// Init all distances with infinity assuming that currently we can't reach
|
||||
// any of the vertices except start one.
|
||||
Object.keys(graph.vertices).forEach((vertexKey) => {
|
||||
distances[vertexKey] = Infinity;
|
||||
});
|
||||
distances[startVertex.getKey()] = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
// Init vertices queue.
|
||||
queue.add(startVertex, distances[startVertex.getKey()]);
|
||||
|
||||
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
|
||||
const currentVertex = queue.poll();
|
||||
|
||||
graph.getNeighbors(currentVertex).forEach((neighbor) => {
|
||||
// Don't visit already visited vertices.
|
||||
if (!visitedVertices[neighbor.getKey()]) {
|
||||
// Update distances to every neighbor from current vertex.
|
||||
const edge = graph.findEdge(currentVertex, neighbor);
|
||||
|
||||
const existingDistanceToNeighbor = distances[neighbor.getKey()];
|
||||
const distanceToNeighborFromCurrent = distances[currentVertex.getKey()] + edge.weight;
|
||||
|
||||
if (distanceToNeighborFromCurrent < existingDistanceToNeighbor) {
|
||||
distances[neighbor.getKey()] = distanceToNeighborFromCurrent;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Add neighbor to the queue for further visiting.
|
||||
queue.add(neighbor, distances[neighbor.getKey()]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
// Add current vertex to visited ones.
|
||||
visitedVertices[currentVertex.getKey()] = currentVertex;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return distances;
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -71,6 +71,7 @@ export default class Graph {
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @param {GraphVertex} startVertex
|
||||
* @param {GraphVertex} endVertex
|
||||
* @return {(GraphEdge|null)}
|
||||
*/
|
||||
findEdge(startVertex, endVertex) {
|
||||
const vertex = this.getVertexByKey(startVertex.getKey());
|
||||
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user