mirror of
https://github.moeyy.xyz/https://github.com/trekhleb/javascript-algorithms.git
synced 2024-12-26 23:21:18 +08:00
Adding K Nearest Neighbor to ML folder in algorithms with README and tests (#592)
* Updated KNN and README * Update README.md * new * new * updated tests * updated knn coverage
This commit is contained in:
parent
802557f1ac
commit
871d20d868
@ -143,6 +143,7 @@ a set of rules that precisely define a sequence of operations.
|
|||||||
* `B` [Caesar Cipher](src/algorithms/cryptography/caesar-cipher) - simple substitution cipher
|
* `B` [Caesar Cipher](src/algorithms/cryptography/caesar-cipher) - simple substitution cipher
|
||||||
* **Machine Learning**
|
* **Machine Learning**
|
||||||
* `B` [NanoNeuron](https://github.com/trekhleb/nano-neuron) - 7 simple JS functions that illustrate how machines can actually learn (forward/backward propagation)
|
* `B` [NanoNeuron](https://github.com/trekhleb/nano-neuron) - 7 simple JS functions that illustrate how machines can actually learn (forward/backward propagation)
|
||||||
|
* `B` [KNN](src/algorithms/ML/KNN) - K Nearest Neighbors
|
||||||
* **Uncategorized**
|
* **Uncategorized**
|
||||||
* `B` [Tower of Hanoi](src/algorithms/uncategorized/hanoi-tower)
|
* `B` [Tower of Hanoi](src/algorithms/uncategorized/hanoi-tower)
|
||||||
* `B` [Square Matrix Rotation](src/algorithms/uncategorized/square-matrix-rotation) - in-place algorithm
|
* `B` [Square Matrix Rotation](src/algorithms/uncategorized/square-matrix-rotation) - in-place algorithm
|
||||||
|
|||||||
23
src/algorithms/ML/KNN/README.md
Normal file
23
src/algorithms/ML/KNN/README.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
|
|||||||
|
# KNN Algorithm
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
KNN stands for K Nearest Neighbors. KNN is a supervised Machine Learning algorithm. It's a classification algorithm, determining the class of a sample vector using a sample data.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
The idea is to calculate the similarity between two data points on the basis of a distance metric. Euclidean distance is used mostly for this task. The algorithm is as follows -
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
1. Check for errors like invalid data/labels.
|
||||||
|
2. Calculate the euclidean distance of all the data points in training data with the classification point
|
||||||
|
3. Sort the distances of points along with their classes in ascending order
|
||||||
|
4. Take the initial "K" classes and find the mode to get the most similar class
|
||||||
|
5. Report the most similar class
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Here is a visualization for better understanding -
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
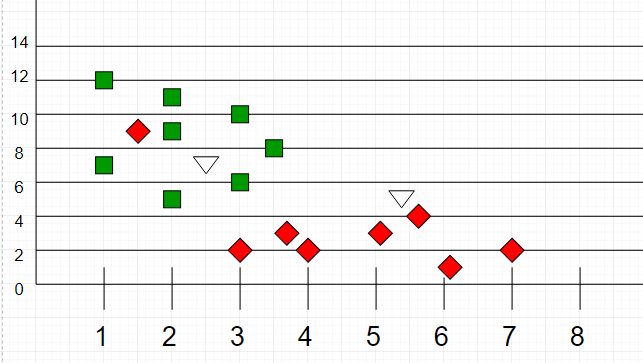
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Here, as we can see, the classification of unknown points will be judged by their proximity to other points.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
It is important to note that "K" is preferred to have odd values in order to break ties. Usually "K" is taken as 3 or 5.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## References
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- [GeeksforGeeks](https://media.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/uploads/graph2-2.png)
|
||||||
42
src/algorithms/ML/KNN/__test__/knn.test.js
Normal file
42
src/algorithms/ML/KNN/__test__/knn.test.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
|
|||||||
|
import KNN from '../knn';
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
describe('KNN', () => {
|
||||||
|
test('should throw an error on invalid data', () => {
|
||||||
|
expect(() => {
|
||||||
|
KNN();
|
||||||
|
}).toThrowError();
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
test('should throw an error on invalid labels', () => {
|
||||||
|
const nolabels = () => {
|
||||||
|
KNN([[1, 1]]);
|
||||||
|
};
|
||||||
|
expect(nolabels).toThrowError();
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
it('should throw an error on not giving classification vector', () => {
|
||||||
|
const noclassification = () => {
|
||||||
|
KNN([[1, 1]], [1]);
|
||||||
|
};
|
||||||
|
expect(noclassification).toThrowError();
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
it('should throw an error on not giving classification vector', () => {
|
||||||
|
const inconsistent = () => {
|
||||||
|
KNN([[1, 1]], [1], [1]);
|
||||||
|
};
|
||||||
|
expect(inconsistent).toThrowError();
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
it('should find the nearest neighbour', () => {
|
||||||
|
let dataX = [[1, 1], [2, 2]];
|
||||||
|
let dataY = [1, 2];
|
||||||
|
expect(KNN(dataX, dataY, [1, 1])).toBe(1);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
dataX = [[1, 1], [6, 2], [3, 3], [4, 5], [9, 2], [2, 4], [8, 7]];
|
||||||
|
dataY = [1, 2, 1, 2, 1, 2, 1];
|
||||||
|
expect(KNN(dataX, dataY, [1.25, 1.25]))
|
||||||
|
.toBe(1);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
dataX = [[1, 1], [6, 2], [3, 3], [4, 5], [9, 2], [2, 4], [8, 7]];
|
||||||
|
dataY = [1, 2, 1, 2, 1, 2, 1];
|
||||||
|
expect(KNN(dataX, dataY, [1.25, 1.25], 5))
|
||||||
|
.toBe(2);
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
60
src/algorithms/ML/KNN/knn.js
Normal file
60
src/algorithms/ML/KNN/knn.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,60 @@
|
|||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* @param {object} dataY
|
||||||
|
* @param {object} dataX
|
||||||
|
* @param {object} toClassify
|
||||||
|
* @param {number} k
|
||||||
|
* @return {number}
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
export default function KNN(dataX, dataY, toClassify, K) {
|
||||||
|
let k = -1;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
if (K === undefined) {
|
||||||
|
k = 3;
|
||||||
|
} else {
|
||||||
|
k = K;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// creating function to calculate the euclidean distance between 2 vectors
|
||||||
|
function euclideanDistance(x1, x2) {
|
||||||
|
// checking errors
|
||||||
|
if (x1.length !== x2.length) {
|
||||||
|
throw new Error('inconsistency between data and classification vector.');
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
// calculate the euclidean distance between 2 vectors and return
|
||||||
|
let totalSSE = 0;
|
||||||
|
for (let j = 0; j < x1.length; j += 1) {
|
||||||
|
totalSSE += (x1[j] - x2[j]) ** 2;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return Number(Math.sqrt(totalSSE).toFixed(2));
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// starting algorithm
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// calculate distance from toClassify to each point for all dimensions in dataX
|
||||||
|
// store distance and point's class_index into distance_class_list
|
||||||
|
let distanceList = [];
|
||||||
|
for (let i = 0; i < dataX.length; i += 1) {
|
||||||
|
const tmStore = [];
|
||||||
|
tmStore.push(euclideanDistance(dataX[i], toClassify));
|
||||||
|
tmStore.push(dataY[i]);
|
||||||
|
distanceList[i] = tmStore;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// sort distanceList
|
||||||
|
// take initial k values, count with class index
|
||||||
|
distanceList = distanceList.sort().slice(0, k);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// count the number of instances of each class in top k members
|
||||||
|
// with that maintain record of highest count class simultanously
|
||||||
|
const modeK = {};
|
||||||
|
const maxm = [-1, -1];
|
||||||
|
for (let i = 0; i < Math.min(k, distanceList.length); i += 1) {
|
||||||
|
if (distanceList[i][1] in modeK) modeK[distanceList[i][1]] += 1;
|
||||||
|
else modeK[distanceList[i][1]] = 1;
|
||||||
|
if (modeK[distanceList[i][1]] > maxm[0]) {
|
||||||
|
[maxm[0], maxm[1]] = [modeK[distanceList[i][1]], distanceList[i][1]];
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
// return the class with highest count from maxm
|
||||||
|
return maxm[1];
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user