mirror of
https://github.moeyy.xyz/https://github.com/trekhleb/javascript-algorithms.git
synced 2024-12-26 15:11:16 +08:00
Adding Sieve of Eratosthenes (#46)
* Adding Sieve of Eratosthenes * Typo
This commit is contained in:
parent
870c3ba2a4
commit
943f83492a
29
src/algorithms/math/sieve-of-eratosthenes/README.md
Normal file
29
src/algorithms/math/sieve-of-eratosthenes/README.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
|
||||
# Sieve of Eratosthenes
|
||||
|
||||
The Sieve of Eratosthenes is an algorithm for finding all prime numbers up to some limit `n`.
|
||||
|
||||
It is attributed to Eratosthenes of Cyrene, an ancient Greek mathematician.
|
||||
|
||||
## How it works
|
||||
|
||||
1. Create a boolean array of `n+1` positions (to represent the numbers `0` through `n`)
|
||||
2. Set positions `0` and `1` to `false`, and the rest to `true`
|
||||
3. Start at position `p = 2` (the first prime number)
|
||||
4. Mark as `false` all the multiples of `p` (that is, positions `2*p`, `3*p`, `4*p`... until you reach the end of the array)
|
||||
5. Find the first position greater than `p` that is `true` in the array. If there is no such position, stop. Otherwise, let `p` equal this new number (which is the next prime), and repeat from step 4
|
||||
|
||||
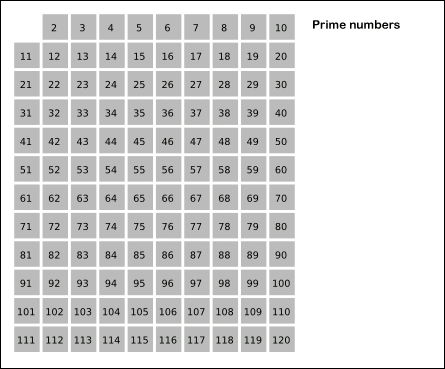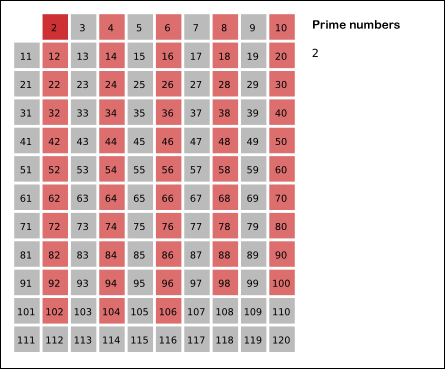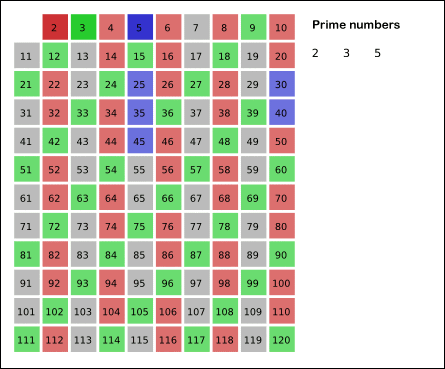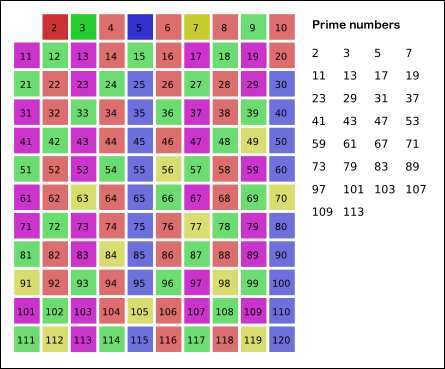
When the algorithm terminates, the numbers remaining `true` in the array are all the primes below `n`.
|
||||
|
||||
An improvement of this algorithm is, in step 4, start marking multiples of `p` from `p*p`, and not from `2*p`. The reason why this works is because, at that point, smaller multiples of `p` will have already been marked `false`.
|
||||
|
||||
## Example
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Complexity
|
||||
|
||||
The algorithm has a complexity of `O(n log(log n))`.
|
||||
|
||||
## References
|
||||
|
||||
[Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sieve_of_Eratosthenes)
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,12 @@
|
||||
import sieveOfEratosthenes from '../sieveOfEratosthenes';
|
||||
|
||||
describe('factorial', () => {
|
||||
it('should find all primes less than or equal to n', () => {
|
||||
expect(sieveOfEratosthenes(5)).toEqual([2, 3, 5]);
|
||||
expect(sieveOfEratosthenes(10)).toEqual([2, 3, 5, 7]);
|
||||
expect(sieveOfEratosthenes(100)).toEqual([
|
||||
2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41,
|
||||
43, 47, 53, 59, 61, 67, 71, 73, 79, 83, 89, 97,
|
||||
]);
|
||||
});
|
||||
});
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,28 @@
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @param {number} n
|
||||
* @return {number[]}
|
||||
*/
|
||||
export default function sieveOfEratosthenes(n) {
|
||||
const isPrime = new Array(n + 1).fill(true);
|
||||
isPrime[0] = false;
|
||||
isPrime[1] = false;
|
||||
const primes = [];
|
||||
|
||||
for (let i = 2; i <= n; i += 1) {
|
||||
if (isPrime[i] === true) {
|
||||
primes.push(i);
|
||||
|
||||
// Warning: When working with really big numbers, the following line may cause overflow
|
||||
// In that case, it can be changed to:
|
||||
// let j = 2 * i;
|
||||
let j = i * i;
|
||||
|
||||
while (j <= n) {
|
||||
isPrime[j] = false;
|
||||
j += i;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return primes;
|
||||
}
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user