mirror of
https://github.moeyy.xyz/https://github.com/trekhleb/javascript-algorithms.git
synced 2024-11-10 11:09:43 +08:00
Merge branch 'master' into my-test
This commit is contained in:
commit
e076e12dee
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
|||||||
|
# @see: https://editorconfig.org/
|
||||||
root = true
|
root = true
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[*]
|
[*]
|
||||||
@ -6,3 +7,4 @@ insert_final_newline = true
|
|||||||
charset = utf-8
|
charset = utf-8
|
||||||
indent_style = space
|
indent_style = space
|
||||||
indent_size = 2
|
indent_size = 2
|
||||||
|
trim_trailing_whitespace = true
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@ -6,7 +6,7 @@
|
|||||||
Este repositorio contiene ejemplos basados en JavaScript de muchos
|
Este repositorio contiene ejemplos basados en JavaScript de muchos
|
||||||
algoritmos y estructuras de datos populares.
|
algoritmos y estructuras de datos populares.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Cada algoritmo y estructura de datos tiene su propio LÉAME con explicaciones relacionadas y
|
Cada algoritmo y estructura de datos tiene su propio LÉAME con explicaciones relacionadas y
|
||||||
enlaces para lecturas adicionales (incluyendo algunas a vídeos de YouTube).
|
enlaces para lecturas adicionales (incluyendo algunas a vídeos de YouTube).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
_Léelo en otros idiomas:_
|
_Léelo en otros idiomas:_
|
||||||
@ -54,7 +54,7 @@ los datos.
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
## Algoritmos
|
## Algoritmos
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Un algoritmo es una especificación inequívoca de cómo resolver una clase de problemas. Es un conjunto de reglas que
|
Un algoritmo es una especificación inequívoca de cómo resolver una clase de problemas. Es un conjunto de reglas que
|
||||||
definen con precisión una secuencia de operaciones.
|
definen con precisión una secuencia de operaciones.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
`P` - Principiante, `A` - Avanzado
|
`P` - Principiante, `A` - Avanzado
|
||||||
@ -231,7 +231,7 @@ npm test -- 'LinkedList'
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
**Campo de juegos**
|
**Campo de juegos**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Puede jugar con estructuras de datos y algoritmos en el archivo `./src/playground/playground.js` y escribir
|
Puede jugar con estructuras de datos y algoritmos en el archivo `./src/playground/playground.js` y escribir
|
||||||
pruebas para ello en `./src/playground/__test__/playground.test.js`.
|
pruebas para ello en `./src/playground/__test__/playground.test.js`.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
A continuación, simplemente ejecute el siguiente comando para comprobar si el código funciona como se espera:
|
A continuación, simplemente ejecute el siguiente comando para comprobar si el código funciona como se espera:
|
||||||
@ -254,7 +254,7 @@ Orden de crecimiento de los algoritmos especificados en la notación O grande.
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
Fuente: [Big O Cheat Sheet](http://bigocheatsheet.com/).
|
Fuente: [Big O Cheat Sheet](http://bigocheatsheet.com/).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
A continuación se muestra la lista de algunas de las notaciones de Big O más utilizadas y sus comparaciones de rendimiento
|
A continuación se muestra la lista de algunas de las notaciones de Big O más utilizadas y sus comparaciones de rendimiento
|
||||||
frente a diferentes tamaños de los datos de entrada.
|
frente a diferentes tamaños de los datos de entrada.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
| Notación O grande | Cálculos para 10 elementos | Cálculos para 100 elementos | Cálculos para 1000 elementos |
|
| Notación O grande | Cálculos para 10 elementos | Cálculos para 100 elementos | Cálculos para 1000 elementos |
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@ -56,7 +56,7 @@ un insieme di regole che definiscono con precisione una sequenza di operazioni.
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
* **Matematica**
|
* **Matematica**
|
||||||
* `P` [Manipolazione dei Bit](src/algorithms/math/bits) - set/get/update/clear bits, moltiplicazione/divisione per due, gestire numeri negativi etc.
|
* `P` [Manipolazione dei Bit](src/algorithms/math/bits) - set/get/update/clear bits, moltiplicazione/divisione per due, gestire numeri negativi etc.
|
||||||
* `P` [Fattoriale](src/algorithms/math/factorial)
|
* `P` [Fattoriale](src/algorithms/math/factorial)
|
||||||
* `P` [Numeri di Fibonacci](src/algorithms/math/fibonacci) - classico e forma chiusa
|
* `P` [Numeri di Fibonacci](src/algorithms/math/fibonacci) - classico e forma chiusa
|
||||||
* `P` [Test di Primalità](src/algorithms/math/primality-test) (metodo del divisore)
|
* `P` [Test di Primalità](src/algorithms/math/primality-test) (metodo del divisore)
|
||||||
* `P` [Algoritmo di Euclide](src/algorithms/math/euclidean-algorithm) - trova il massimo comune divisore (MCD)
|
* `P` [Algoritmo di Euclide](src/algorithms/math/euclidean-algorithm) - trova il massimo comune divisore (MCD)
|
||||||
@ -64,13 +64,13 @@ un insieme di regole che definiscono con precisione una sequenza di operazioni.
|
|||||||
* `P` [Crivello di Eratostene](src/algorithms/math/sieve-of-eratosthenes) - trova i numeri i primi fino al limite indicato
|
* `P` [Crivello di Eratostene](src/algorithms/math/sieve-of-eratosthenes) - trova i numeri i primi fino al limite indicato
|
||||||
* `P` [Potenza di due](src/algorithms/math/is-power-of-two) - controlla se il numero è una potenza di due
|
* `P` [Potenza di due](src/algorithms/math/is-power-of-two) - controlla se il numero è una potenza di due
|
||||||
* `P` [Triangolo di Pascal](src/algorithms/math/pascal-triangle)
|
* `P` [Triangolo di Pascal](src/algorithms/math/pascal-triangle)
|
||||||
* `P` [Numeri Complessi](src/algorithms/math/complex-number) - numeri complessi e operazioni
|
* `P` [Numeri Complessi](src/algorithms/math/complex-number) - numeri complessi e operazioni
|
||||||
* `P` [Radiante & Gradi](src/algorithms/math/radian) - conversione da radiante a gradi e viceversa
|
* `P` [Radiante & Gradi](src/algorithms/math/radian) - conversione da radiante a gradi e viceversa
|
||||||
* `P` [Potenza di un Numero](src/algorithms/math/fast-powering)
|
* `P` [Potenza di un Numero](src/algorithms/math/fast-powering)
|
||||||
* `A` [Partizione di un Intero](src/algorithms/math/integer-partition)
|
* `A` [Partizione di un Intero](src/algorithms/math/integer-partition)
|
||||||
* `A` [Radice Quadrata](src/algorithms/math/square-root) - Metodo di Newton
|
* `A` [Radice Quadrata](src/algorithms/math/square-root) - Metodo di Newton
|
||||||
* `A` [Algoritmo di Liu Hui π](src/algorithms/math/liu-hui) - calcolare π usando un poligono
|
* `A` [Algoritmo di Liu Hui π](src/algorithms/math/liu-hui) - calcolare π usando un poligono
|
||||||
* `A` [Trasformata Discreta di Fourier ](src/algorithms/math/fourier-transform) -decomporre una funzione di tempo (un segnale) nelle frequenze che lo compongono
|
* `A` [Trasformata Discreta di Fourier ](src/algorithms/math/fourier-transform) -decomporre una funzione di tempo (un segnale) nelle frequenze che lo compongono
|
||||||
* **Set**
|
* **Set**
|
||||||
* `P` [Prodotto Cartesiano](src/algorithms/sets/cartesian-product) - moltiplicazione multipla di set
|
* `P` [Prodotto Cartesiano](src/algorithms/sets/cartesian-product) - moltiplicazione multipla di set
|
||||||
* `P` [Fisher–Yates Shuffle](src/algorithms/sets/fisher-yates) - permutazione casuale di un sequenza finita
|
* `P` [Fisher–Yates Shuffle](src/algorithms/sets/fisher-yates) - permutazione casuale di un sequenza finita
|
||||||
@ -116,8 +116,8 @@ un insieme di regole che definiscono con precisione una sequenza di operazioni.
|
|||||||
* `P` [Ricerca in Profondità su Grafi](src/algorithms/graph/depth-first-search) (DFS)
|
* `P` [Ricerca in Profondità su Grafi](src/algorithms/graph/depth-first-search) (DFS)
|
||||||
* `P` [Breadth-First Search su Grafi](src/algorithms/graph/breadth-first-search) (BFS)
|
* `P` [Breadth-First Search su Grafi](src/algorithms/graph/breadth-first-search) (BFS)
|
||||||
* `P` [Algoritmo di Kruskal](src/algorithms/graph/kruskal) - ricerca dell'Albero con Minima Distanza (MST) per grafi pesati unidirezionali
|
* `P` [Algoritmo di Kruskal](src/algorithms/graph/kruskal) - ricerca dell'Albero con Minima Distanza (MST) per grafi pesati unidirezionali
|
||||||
* `A` [Algoritmo di Dijkstra](src/algorithms/graph/dijkstra) - ricerca dei percorsi più breve per raggiungere tutti i vertici del grafo da un singolo vertice
|
* `A` [Algoritmo di Dijkstra](src/algorithms/graph/dijkstra) - ricerca dei percorsi più breve per raggiungere tutti i vertici del grafo da un singolo vertice
|
||||||
* `A` [Algoritmo di Bellman-Ford](src/algorithms/graph/bellman-ford) - ricerca dei percorsi più breve per raggiungere tutti i vertici del grafo da un singolo vertice
|
* `A` [Algoritmo di Bellman-Ford](src/algorithms/graph/bellman-ford) - ricerca dei percorsi più breve per raggiungere tutti i vertici del grafo da un singolo vertice
|
||||||
* `A` [Algoritmo di Floyd-Warshall](src/algorithms/graph/floyd-warshall) - ricerca dei percorsi più brevi tra tutte le coppie di vertici
|
* `A` [Algoritmo di Floyd-Warshall](src/algorithms/graph/floyd-warshall) - ricerca dei percorsi più brevi tra tutte le coppie di vertici
|
||||||
* `A` [Rivelamento dei Cicli](src/algorithms/graph/detect-cycle) - per grafici diretti e non diretti (basate su partizioni DFS e Disjoint Set)
|
* `A` [Rivelamento dei Cicli](src/algorithms/graph/detect-cycle) - per grafici diretti e non diretti (basate su partizioni DFS e Disjoint Set)
|
||||||
* `A` [Algoritmo di Prim](src/algorithms/graph/prim) - ricerca dell'Albero Ricoprente Minimo (MST) per grafi unidirezionali pesati
|
* `A` [Algoritmo di Prim](src/algorithms/graph/prim) - ricerca dell'Albero Ricoprente Minimo (MST) per grafi unidirezionali pesati
|
||||||
@ -129,12 +129,12 @@ un insieme di regole che definiscono con precisione una sequenza di operazioni.
|
|||||||
* `A` [Componenti Fortemente Connessa](src/algorithms/graph/strongly-connected-components) - algoritmo di Kosaraju
|
* `A` [Componenti Fortemente Connessa](src/algorithms/graph/strongly-connected-components) - algoritmo di Kosaraju
|
||||||
* `A` [Problema del Commesso Viaggiatore](src/algorithms/graph/travelling-salesman) - il percorso più breve che visita ogni città e ritorna alla città iniziale
|
* `A` [Problema del Commesso Viaggiatore](src/algorithms/graph/travelling-salesman) - il percorso più breve che visita ogni città e ritorna alla città iniziale
|
||||||
* **Crittografia**
|
* **Crittografia**
|
||||||
* `P` [Hash Polinomiale](src/algorithms/cryptography/polynomial-hash) - Una funzione hash di rolling basata sul polinomio
|
* `P` [Hash Polinomiale](src/algorithms/cryptography/polynomial-hash) - Una funzione hash di rolling basata sul polinomio
|
||||||
* **Senza categoria**
|
* **Senza categoria**
|
||||||
* `P` [Torre di Hanoi](src/algorithms/uncategorized/hanoi-tower)
|
* `P` [Torre di Hanoi](src/algorithms/uncategorized/hanoi-tower)
|
||||||
* `P` [Rotazione Matrice Quadrata](src/algorithms/uncategorized/square-matrix-rotation) - algoritmo in memoria
|
* `P` [Rotazione Matrice Quadrata](src/algorithms/uncategorized/square-matrix-rotation) - algoritmo in memoria
|
||||||
* `P` [Jump Game](src/algorithms/uncategorized/jump-game) - backtracking, programmazione dinamica (top-down + bottom-up) ed esempre di greeedy
|
* `P` [Jump Game](src/algorithms/uncategorized/jump-game) - backtracking, programmazione dinamica (top-down + bottom-up) ed esempre di greeedy
|
||||||
* `P` [Percorsi Unici](src/algorithms/uncategorized/unique-paths) - backtracking, programmazione dinamica and l'esempio del Triangolo di Pascal
|
* `P` [Percorsi Unici](src/algorithms/uncategorized/unique-paths) - backtracking, programmazione dinamica and l'esempio del Triangolo di Pascal
|
||||||
* `P` [Rain Terraces](src/algorithms/uncategorized/rain-terraces) - problema dell'acqua piovana in trappola(versione con programmazione dinamica e brute force)
|
* `P` [Rain Terraces](src/algorithms/uncategorized/rain-terraces) - problema dell'acqua piovana in trappola(versione con programmazione dinamica e brute force)
|
||||||
* `P` [Recursive Staircase](src/algorithms/uncategorized/recursive-staircase) - contare il numero di percorsi per arrivare in vetta(4 soluzioni)
|
* `P` [Recursive Staircase](src/algorithms/uncategorized/recursive-staircase) - contare il numero di percorsi per arrivare in vetta(4 soluzioni)
|
||||||
* `A` [Rompicapo delle Otto Regine](src/algorithms/uncategorized/n-queens)
|
* `A` [Rompicapo delle Otto Regine](src/algorithms/uncategorized/n-queens)
|
||||||
@ -151,14 +151,14 @@ un insieme di regole che definiscono con precisione una sequenza di operazioni.
|
|||||||
* `P` [Recursive Staircase](src/algorithms/uncategorized/recursive-staircase) - contare il numero di percorsi per arrivare in vetta
|
* `P` [Recursive Staircase](src/algorithms/uncategorized/recursive-staircase) - contare il numero di percorsi per arrivare in vetta
|
||||||
* `A` [Massimo SubArray](src/algorithms/sets/maximum-subarray)
|
* `A` [Massimo SubArray](src/algorithms/sets/maximum-subarray)
|
||||||
* `A` [Problema del commesso viaggiatore](src/algorithms/graph/travelling-salesman) - il percorso più breve che visita ogni città e ritorna alla città iniziale
|
* `A` [Problema del commesso viaggiatore](src/algorithms/graph/travelling-salesman) - il percorso più breve che visita ogni città e ritorna alla città iniziale
|
||||||
* `A` [Trasformata Discreta di Fourier](src/algorithms/math/fourier-transform) - scomporre la funzione (segnale) del tempo in frequenze che la compongono
|
* `A` [Trasformata Discreta di Fourier](src/algorithms/math/fourier-transform) - scomporre la funzione (segnale) del tempo in frequenze che la compongono
|
||||||
* **Greedy** - scegliere l'opzione migliore al momento d'eleborazione dell'algoritmo, senza alcuna considerazione per il futuro
|
* **Greedy** - scegliere l'opzione migliore al momento d'eleborazione dell'algoritmo, senza alcuna considerazione per il futuro
|
||||||
* `P` [Jump Game](src/algorithms/uncategorized/jump-game)
|
* `P` [Jump Game](src/algorithms/uncategorized/jump-game)
|
||||||
* `A` [Problema dello Zaino di Knapsack](src/algorithms/sets/knapsack-problem)
|
* `A` [Problema dello Zaino di Knapsack](src/algorithms/sets/knapsack-problem)
|
||||||
* `A` [Algoritmo di Dijkstra](src/algorithms/graph/dijkstra) - ricerca del percorso più breve tra tutti i vertici del grafo
|
* `A` [Algoritmo di Dijkstra](src/algorithms/graph/dijkstra) - ricerca del percorso più breve tra tutti i vertici del grafo
|
||||||
* `A` [Algoritmo di Prim](src/algorithms/graph/prim) - ricerca del Minimo Albero Ricoprente per grafi pesati e unidirezionali
|
* `A` [Algoritmo di Prim](src/algorithms/graph/prim) - ricerca del Minimo Albero Ricoprente per grafi pesati e unidirezionali
|
||||||
* `A` [Kruskal’s Algorithm](src/algorithms/graph/kruskal) - finding Minimum Spanning Tree (MST) for weighted undirected graph
|
* `A` [Kruskal’s Algorithm](src/algorithms/graph/kruskal) - finding Minimum Spanning Tree (MST) for weighted undirected graph
|
||||||
* **Divide e Conquista** - divide il problema in piccole parti e risolve ogni parte
|
* **Divide e Conquista** - divide il problema in piccole parti e risolve ogni parte
|
||||||
* `P` [Ricerca Binaria](src/algorithms/search/binary-search)
|
* `P` [Ricerca Binaria](src/algorithms/search/binary-search)
|
||||||
* `P` [Torre di Hanoi](src/algorithms/uncategorized/hanoi-tower)
|
* `P` [Torre di Hanoi](src/algorithms/uncategorized/hanoi-tower)
|
||||||
* `P` [Triangolo di Pascal](src/algorithms/math/pascal-triangle)
|
* `P` [Triangolo di Pascal](src/algorithms/math/pascal-triangle)
|
||||||
@ -186,7 +186,7 @@ un insieme di regole che definiscono con precisione una sequenza di operazioni.
|
|||||||
* `A` [Partizione di un Intero](src/algorithms/math/integer-partition)
|
* `A` [Partizione di un Intero](src/algorithms/math/integer-partition)
|
||||||
* `A` [Massimo SubArray](src/algorithms/sets/maximum-subarray)
|
* `A` [Massimo SubArray](src/algorithms/sets/maximum-subarray)
|
||||||
* `A` [Algoritmo di Bellman-Ford](src/algorithms/graph/bellman-ford) - ricerca del percorso più breve per tutti i vertici del grafo
|
* `A` [Algoritmo di Bellman-Ford](src/algorithms/graph/bellman-ford) - ricerca del percorso più breve per tutti i vertici del grafo
|
||||||
* `A` [Algoritmo di Floyd-Warshall](src/algorithms/graph/floyd-warshall) - ricerca del percorso più breve tra tutte le coppie di vertici
|
* `A` [Algoritmo di Floyd-Warshall](src/algorithms/graph/floyd-warshall) - ricerca del percorso più breve tra tutte le coppie di vertici
|
||||||
* `A` [Espressioni Regolari](src/algorithms/string/regular-expression-matching)
|
* `A` [Espressioni Regolari](src/algorithms/string/regular-expression-matching)
|
||||||
* **Backtracking** - come la brute force, provate a generare tutte le soluzioni possibili, ma ogni volta che generate la prossima soluzione testate se soddisfa tutte le condizioni e solo allora continuare a generare soluzioni successive. Altrimenti, fate marcia indietro, e andate su un percorso diverso per trovare una soluzione. Normalmente si utilizza l'algoritmo DFS.
|
* **Backtracking** - come la brute force, provate a generare tutte le soluzioni possibili, ma ogni volta che generate la prossima soluzione testate se soddisfa tutte le condizioni e solo allora continuare a generare soluzioni successive. Altrimenti, fate marcia indietro, e andate su un percorso diverso per trovare una soluzione. Normalmente si utilizza l'algoritmo DFS.
|
||||||
* `P` [Jump Game](src/algorithms/uncategorized/jump-game)
|
* `P` [Jump Game](src/algorithms/uncategorized/jump-game)
|
||||||
@ -228,10 +228,10 @@ npm test -- 'LinkedList'
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
**Playground**
|
**Playground**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Se vuoi puoi giocare le strutture dati e gli algoritmi nel file ./src/playground/playground.js` e
|
Se vuoi puoi giocare le strutture dati e gli algoritmi nel file ./src/playground/playground.js` e
|
||||||
scrivere test nel file `./src/playground/__test__/playground.test.js`.
|
scrivere test nel file `./src/playground/__test__/playground.test.js`.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Poi puoi semplicemente eseguire il seguente comando per testare quello che hai scritto :
|
Poi puoi semplicemente eseguire il seguente comando per testare quello che hai scritto :
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
npm test -- 'playground'
|
npm test -- 'playground'
|
||||||
@ -243,9 +243,9 @@ npm test -- 'playground'
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
[▶ Data Structures and Algorithms on YouTube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLLXdhg_r2hKA7DPDsunoDZ-Z769jWn4R8)
|
[▶ Data Structures and Algorithms on YouTube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLLXdhg_r2hKA7DPDsunoDZ-Z769jWn4R8)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Notazione Big O
|
### Notazione Big O
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
* La notazione Big O* è usata per classificare algoritmi in base al tempo di esecuzione o ai
|
* La notazione Big O* è usata per classificare algoritmi in base al tempo di esecuzione o ai
|
||||||
requisiti di spazio che crescono in base alla crescita dell'input .
|
requisiti di spazio che crescono in base alla crescita dell'input .
|
||||||
Nella grafico qua sotto puoi trovare gli ordini di crescita più comuni degli algoritmi usando la notazione Big O.
|
Nella grafico qua sotto puoi trovare gli ordini di crescita più comuni degli algoritmi usando la notazione Big O.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@ -60,7 +60,7 @@ _Read this in other languages:_
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
* **数学**
|
* **数学**
|
||||||
* `B` [ビット操作](src/algorithms/math/bits) - set/get/update/clear bits, 2つの乗算/除算, 否定的にする. 等
|
* `B` [ビット操作](src/algorithms/math/bits) - set/get/update/clear bits, 2つの乗算/除算, 否定的にする. 等
|
||||||
* `B` [因果関係](src/algorithms/math/factorial)
|
* `B` [因果関係](src/algorithms/math/factorial)
|
||||||
* `B` [フィボナッチ数](src/algorithms/math/fibonacci) - クラシックとクローズドフォームのバージョン
|
* `B` [フィボナッチ数](src/algorithms/math/fibonacci) - クラシックとクローズドフォームのバージョン
|
||||||
* `B` [素数性テスト](src/algorithms/math/primality-test) (trial division 方法)
|
* `B` [素数性テスト](src/algorithms/math/primality-test) (trial division 方法)
|
||||||
* `B` [ユークリッドアルゴリズム](src/algorithms/math/euclidean-algorithm) - 最大公約数を計算する (GCD)
|
* `B` [ユークリッドアルゴリズム](src/algorithms/math/euclidean-algorithm) - 最大公約数を計算する (GCD)
|
||||||
@ -118,7 +118,7 @@ _Read this in other languages:_
|
|||||||
* **グラフ**
|
* **グラフ**
|
||||||
* `B` [深度優先検索](src/algorithms/graph/depth-first-search) (DFS)
|
* `B` [深度優先検索](src/algorithms/graph/depth-first-search) (DFS)
|
||||||
* `B` [幅優先検索](src/algorithms/graph/breadth-first-search) (BFS)
|
* `B` [幅優先検索](src/algorithms/graph/breadth-first-search) (BFS)
|
||||||
* `B` [Kruskalのアルゴリズム](src/algorithms/graph/kruskal) - 重み付き無向グラフの最小スパニングツリー(MST)の発見
|
* `B` [Kruskalのアルゴリズム](src/algorithms/graph/kruskal) - 重み付き無向グラフの最小スパニングツリー(MST)の発見
|
||||||
* `A` [Dijkstraアルゴリズム](src/algorithms/graph/dijkstra) - 単一の頂点からすべてのグラフ頂点への最短経路を見つける
|
* `A` [Dijkstraアルゴリズム](src/algorithms/graph/dijkstra) - 単一の頂点からすべてのグラフ頂点への最短経路を見つける
|
||||||
* `A` [Bellman-Fordアルゴリズム](src/algorithms/graph/bellman-ford) - 単一の頂点からすべてのグラフ頂点への最短経路を見つける
|
* `A` [Bellman-Fordアルゴリズム](src/algorithms/graph/bellman-ford) - 単一の頂点からすべてのグラフ頂点への最短経路を見つける
|
||||||
* `A` [Floyd-Warshallアルゴリズム](src/algorithms/graph/floyd-warshall) - すべての頂点ペア間の最短経路を見つける
|
* `A` [Floyd-Warshallアルゴリズム](src/algorithms/graph/floyd-warshall) - すべての頂点ペア間の最短経路を見つける
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@ -25,7 +25,7 @@ _Read this in other languages:_
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
자료 구조는 데이터를 특정 방식으로 구성하고 저장함으로써 더 효율적으로
|
자료 구조는 데이터를 특정 방식으로 구성하고 저장함으로써 더 효율적으로
|
||||||
접근하고 수정할 수 있게 해줍니다. 간단히 말해, 자료 구조는 데이터 값들,
|
접근하고 수정할 수 있게 해줍니다. 간단히 말해, 자료 구조는 데이터 값들,
|
||||||
데이터 간의 관계, 그리고 데이터를 다룰 수 있는 함수와 작업의 모임입니다.
|
데이터 간의 관계, 그리고 데이터를 다룰 수 있는 함수와 작업의 모임입니다.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
`B` - 입문자, `A` - 숙련자
|
`B` - 입문자, `A` - 숙련자
|
||||||
@ -50,8 +50,8 @@ _Read this in other languages:_
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
## 알고리즘
|
## 알고리즘
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
알고리즘은 어떤 종류의 문제를 풀 수 있는 정확한 방법이며,
|
알고리즘은 어떤 종류의 문제를 풀 수 있는 정확한 방법이며,
|
||||||
일련의 작업을 정확하게 정의해 놓은 규칙들입니다.
|
일련의 작업을 정확하게 정의해 놓은 규칙들입니다.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
`B` - 입문자, `A` - 숙련자
|
`B` - 입문자, `A` - 숙련자
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@ -59,7 +59,7 @@ _Read this in other languages:_
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
* **Math**
|
* **Math**
|
||||||
* `B` [Bit Manipulation](src/algorithms/math/bits) - set/get/update/clear bits, 2의 곱 / 나누기, 음수로 만들기 etc.
|
* `B` [Bit Manipulation](src/algorithms/math/bits) - set/get/update/clear bits, 2의 곱 / 나누기, 음수로 만들기 etc.
|
||||||
* `B` [팩토리얼](src/algorithms/math/factorial)
|
* `B` [팩토리얼](src/algorithms/math/factorial)
|
||||||
* `B` [피보나치 수](src/algorithms/math/fibonacci)
|
* `B` [피보나치 수](src/algorithms/math/fibonacci)
|
||||||
* `B` [소수 판별](src/algorithms/math/primality-test) (trial division 방식)
|
* `B` [소수 판별](src/algorithms/math/primality-test) (trial division 방식)
|
||||||
* `B` [유클리드 호제법](src/algorithms/math/euclidean-algorithm) - 최대공약수 (GCD)
|
* `B` [유클리드 호제법](src/algorithms/math/euclidean-algorithm) - 최대공약수 (GCD)
|
||||||
@ -126,7 +126,7 @@ _Read this in other languages:_
|
|||||||
* **Uncategorized**
|
* **Uncategorized**
|
||||||
* `B` [하노이 탑](src/algorithms/uncategorized/hanoi-tower)
|
* `B` [하노이 탑](src/algorithms/uncategorized/hanoi-tower)
|
||||||
* `B` [정방 행렬 회전](src/algorithms/uncategorized/square-matrix-rotation) - 제자리(in-place) 알고리즘
|
* `B` [정방 행렬 회전](src/algorithms/uncategorized/square-matrix-rotation) - 제자리(in-place) 알고리즘
|
||||||
* `B` [점프 게임](src/algorithms/uncategorized/jump-game) - 백트래킹, 동적계획법 (top-down + bottom-up), 탐욕 알고리즘 예제
|
* `B` [점프 게임](src/algorithms/uncategorized/jump-game) - 백트래킹, 동적계획법 (top-down + bottom-up), 탐욕 알고리즘 예제
|
||||||
* `B` [Unique 경로](src/algorithms/uncategorized/unique-paths) - 백트래킹, 동적계획법, 파스칼 삼각형에 기반한 예제
|
* `B` [Unique 경로](src/algorithms/uncategorized/unique-paths) - 백트래킹, 동적계획법, 파스칼 삼각형에 기반한 예제
|
||||||
* `B` [빗물 담기 문제](src/algorithms/uncategorized/rain-terraces) - trapping rain water problem (동적계획법, 브루트포스 버전)
|
* `B` [빗물 담기 문제](src/algorithms/uncategorized/rain-terraces) - trapping rain water problem (동적계획법, 브루트포스 버전)
|
||||||
* `A` [N-Queens 문제](src/algorithms/uncategorized/n-queens)
|
* `A` [N-Queens 문제](src/algorithms/uncategorized/n-queens)
|
||||||
|
|||||||
13
README.md
13
README.md
@ -23,7 +23,7 @@ _Read this in other languages:_
|
|||||||
[_Türk_](README.tr-TR.md),
|
[_Türk_](README.tr-TR.md),
|
||||||
[_Italiana_](README.it-IT.md)
|
[_Italiana_](README.it-IT.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
*☝ Note that this project is meant to be used for learning and researching purposes
|
*☝ Note that this project is meant to be used for learning and researching purposes
|
||||||
only, and it is **not** meant to be used for production.*
|
only, and it is **not** meant to be used for production.*
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Data Structures
|
## Data Structures
|
||||||
@ -64,9 +64,9 @@ a set of rules that precisely define a sequence of operations.
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
* **Math**
|
* **Math**
|
||||||
* `B` [Bit Manipulation](src/algorithms/math/bits) - set/get/update/clear bits, multiplication/division by two, make negative etc.
|
* `B` [Bit Manipulation](src/algorithms/math/bits) - set/get/update/clear bits, multiplication/division by two, make negative etc.
|
||||||
* `B` [Factorial](src/algorithms/math/factorial)
|
* `B` [Factorial](src/algorithms/math/factorial)
|
||||||
* `B` [Fibonacci Number](src/algorithms/math/fibonacci) - classic and closed-form versions
|
* `B` [Fibonacci Number](src/algorithms/math/fibonacci) - classic and closed-form versions
|
||||||
* `B` [Prime Factors](src/algorithms/math/prime-factors) - finding prime factors and counting them using Hardy-Ramanujan's theorem
|
* `B` [Prime Factors](src/algorithms/math/prime-factors) - finding prime factors and counting them using Hardy-Ramanujan's theorem
|
||||||
* `B` [Primality Test](src/algorithms/math/primality-test) (trial division method)
|
* `B` [Primality Test](src/algorithms/math/primality-test) (trial division method)
|
||||||
* `B` [Euclidean Algorithm](src/algorithms/math/euclidean-algorithm) - calculate the Greatest Common Divisor (GCD)
|
* `B` [Euclidean Algorithm](src/algorithms/math/euclidean-algorithm) - calculate the Greatest Common Divisor (GCD)
|
||||||
* `B` [Least Common Multiple](src/algorithms/math/least-common-multiple) (LCM)
|
* `B` [Least Common Multiple](src/algorithms/math/least-common-multiple) (LCM)
|
||||||
@ -80,7 +80,7 @@ a set of rules that precisely define a sequence of operations.
|
|||||||
* `A` [Integer Partition](src/algorithms/math/integer-partition)
|
* `A` [Integer Partition](src/algorithms/math/integer-partition)
|
||||||
* `A` [Square Root](src/algorithms/math/square-root) - Newton's method
|
* `A` [Square Root](src/algorithms/math/square-root) - Newton's method
|
||||||
* `A` [Liu Hui π Algorithm](src/algorithms/math/liu-hui) - approximate π calculations based on N-gons
|
* `A` [Liu Hui π Algorithm](src/algorithms/math/liu-hui) - approximate π calculations based on N-gons
|
||||||
* `A` [Discrete Fourier Transform](src/algorithms/math/fourier-transform) - decompose a function of time (a signal) into the frequencies that make it up
|
* `A` [Discrete Fourier Transform](src/algorithms/math/fourier-transform) - decompose a function of time (a signal) into the frequencies that make it up
|
||||||
* **Sets**
|
* **Sets**
|
||||||
* `B` [Cartesian Product](src/algorithms/sets/cartesian-product) - product of multiple sets
|
* `B` [Cartesian Product](src/algorithms/sets/cartesian-product) - product of multiple sets
|
||||||
* `B` [Fisher–Yates Shuffle](src/algorithms/sets/fisher-yates) - random permutation of a finite sequence
|
* `B` [Fisher–Yates Shuffle](src/algorithms/sets/fisher-yates) - random permutation of a finite sequence
|
||||||
@ -143,11 +143,12 @@ a set of rules that precisely define a sequence of operations.
|
|||||||
* `B` [Caesar Cipher](src/algorithms/cryptography/caesar-cipher) - simple substitution cipher
|
* `B` [Caesar Cipher](src/algorithms/cryptography/caesar-cipher) - simple substitution cipher
|
||||||
* **Machine Learning**
|
* **Machine Learning**
|
||||||
* `B` [NanoNeuron](https://github.com/trekhleb/nano-neuron) - 7 simple JS functions that illustrate how machines can actually learn (forward/backward propagation)
|
* `B` [NanoNeuron](https://github.com/trekhleb/nano-neuron) - 7 simple JS functions that illustrate how machines can actually learn (forward/backward propagation)
|
||||||
|
* `B` [k-NN](src/algorithms/ml/knn) - k-nearest neighbors classification algorithm
|
||||||
* **Uncategorized**
|
* **Uncategorized**
|
||||||
* `B` [Tower of Hanoi](src/algorithms/uncategorized/hanoi-tower)
|
* `B` [Tower of Hanoi](src/algorithms/uncategorized/hanoi-tower)
|
||||||
* `B` [Square Matrix Rotation](src/algorithms/uncategorized/square-matrix-rotation) - in-place algorithm
|
* `B` [Square Matrix Rotation](src/algorithms/uncategorized/square-matrix-rotation) - in-place algorithm
|
||||||
* `B` [Jump Game](src/algorithms/uncategorized/jump-game) - backtracking, dynamic programming (top-down + bottom-up) and greedy examples
|
* `B` [Jump Game](src/algorithms/uncategorized/jump-game) - backtracking, dynamic programming (top-down + bottom-up) and greedy examples
|
||||||
* `B` [Unique Paths](src/algorithms/uncategorized/unique-paths) - backtracking, dynamic programming and Pascal's Triangle based examples
|
* `B` [Unique Paths](src/algorithms/uncategorized/unique-paths) - backtracking, dynamic programming and Pascal's Triangle based examples
|
||||||
* `B` [Rain Terraces](src/algorithms/uncategorized/rain-terraces) - trapping rain water problem (dynamic programming and brute force versions)
|
* `B` [Rain Terraces](src/algorithms/uncategorized/rain-terraces) - trapping rain water problem (dynamic programming and brute force versions)
|
||||||
* `B` [Recursive Staircase](src/algorithms/uncategorized/recursive-staircase) - count the number of ways to reach to the top (4 solutions)
|
* `B` [Recursive Staircase](src/algorithms/uncategorized/recursive-staircase) - count the number of ways to reach to the top (4 solutions)
|
||||||
* `A` [N-Queens Problem](src/algorithms/uncategorized/n-queens)
|
* `A` [N-Queens Problem](src/algorithms/uncategorized/n-queens)
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@ -3,11 +3,11 @@
|
|||||||
[](https://github.com/trekhleb/javascript-algorithms/actions)
|
[](https://github.com/trekhleb/javascript-algorithms/actions)
|
||||||
[](https://codecov.io/gh/trekhleb/javascript-algorithms)
|
[](https://codecov.io/gh/trekhleb/javascript-algorithms)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
To repozytorium zawiera wiele przykładów JavaScript opartych na
|
To repozytorium zawiera wiele przykładów JavaScript opartych na
|
||||||
znanych algorytmach i strukturach danych.
|
znanych algorytmach i strukturach danych.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Każdy algorytm i struktura danych zawiera osobny plik README
|
Każdy algorytm i struktura danych zawiera osobny plik README
|
||||||
wraz z powiązanymi wyjaśnieniami i odnośnikami do dalszego czytania
|
wraz z powiązanymi wyjaśnieniami i odnośnikami do dalszego czytania
|
||||||
(włącznie z tymi do YouTube videos).
|
(włącznie z tymi do YouTube videos).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
_Read this in other languages:_
|
_Read this in other languages:_
|
||||||
@ -25,10 +25,10 @@ _Read this in other languages:_
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
## Struktury Danych
|
## Struktury Danych
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Struktura danych to sposób uporządkowania i przechowywania informacji w
|
Struktura danych to sposób uporządkowania i przechowywania informacji w
|
||||||
komputerze żeby mogłaby być sprawnie dostępna i efektywnie zmodyfikowana.
|
komputerze żeby mogłaby być sprawnie dostępna i efektywnie zmodyfikowana.
|
||||||
Dokładniej, struktura danych jest zbiorem wartości danych, relacjami
|
Dokładniej, struktura danych jest zbiorem wartości danych, relacjami
|
||||||
pomiędzy nimi, zadaniami lub działaniami, które mogą dotyczyć danych.
|
pomiędzy nimi, zadaniami lub działaniami, które mogą dotyczyć danych.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
`B` - Początkujący, `A` - Zaawansowany
|
`B` - Początkujący, `A` - Zaawansowany
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@ -52,8 +52,8 @@ pomiędzy nimi, zadaniami lub działaniami, które mogą dotyczyć danych.
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
## Algorytmy
|
## Algorytmy
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Algorytm jest to skończony ciąg jasno zdefiniowanych czynności, koniecznych
|
Algorytm jest to skończony ciąg jasno zdefiniowanych czynności, koniecznych
|
||||||
do wykonania pewnego rodzaju zadań. Sposób postępowania prowadzący do
|
do wykonania pewnego rodzaju zadań. Sposób postępowania prowadzący do
|
||||||
rozwiązania problemu.
|
rozwiązania problemu.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
`B` - Początkujący, `A` - Zaawansowany
|
`B` - Początkujący, `A` - Zaawansowany
|
||||||
@ -62,7 +62,7 @@ rozwiązania problemu.
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
* **Matematyka**
|
* **Matematyka**
|
||||||
* `B` [Manipulacja Bitami](src/algorithms/math/bits) - ustaw / uzyskaj / aktualizuj / usuwaj bity, mnożenie / dzielenie przez dwa, tworzenie negatywów itp.
|
* `B` [Manipulacja Bitami](src/algorithms/math/bits) - ustaw / uzyskaj / aktualizuj / usuwaj bity, mnożenie / dzielenie przez dwa, tworzenie negatywów itp.
|
||||||
* `B` [Silna](src/algorithms/math/factorial)
|
* `B` [Silna](src/algorithms/math/factorial)
|
||||||
* `B` [Ciąg Fibonacciego](src/algorithms/math/fibonacci)
|
* `B` [Ciąg Fibonacciego](src/algorithms/math/fibonacci)
|
||||||
* `B` [Test Pierwszorzędności](src/algorithms/math/primality-test) (metoda podziału na próby)
|
* `B` [Test Pierwszorzędności](src/algorithms/math/primality-test) (metoda podziału na próby)
|
||||||
* `B` [Algorytm Euclideana](src/algorithms/math/euclidean-algorithm) - obliczyć Największy Wspólny Dzielnik (GCD)
|
* `B` [Algorytm Euclideana](src/algorithms/math/euclidean-algorithm) - obliczyć Największy Wspólny Dzielnik (GCD)
|
||||||
@ -81,9 +81,9 @@ rozwiązania problemu.
|
|||||||
* `A` [Najdłuższa Wspólna Podsekwencja](src/algorithms/sets/longest-common-subsequence) (LCS)
|
* `A` [Najdłuższa Wspólna Podsekwencja](src/algorithms/sets/longest-common-subsequence) (LCS)
|
||||||
* `A` [Najdłuższa Wzrostająca Podsekwencja](src/algorithms/sets/longest-increasing-subsequence)
|
* `A` [Najdłuższa Wzrostająca Podsekwencja](src/algorithms/sets/longest-increasing-subsequence)
|
||||||
* `A` [Najkrótsza Wspólna Supersekwencja](src/algorithms/sets/shortest-common-supersequence) (SCS)
|
* `A` [Najkrótsza Wspólna Supersekwencja](src/algorithms/sets/shortest-common-supersequence) (SCS)
|
||||||
* `A` [Problem Knapsacka](src/algorithms/sets/knapsack-problem) - "0/1" i "Rozwiązany"
|
* `A` [Problem Knapsacka](src/algorithms/sets/knapsack-problem) - "0/1" i "Rozwiązany"
|
||||||
* `A` [Maksymalna Podtablica](src/algorithms/sets/maximum-subarray) - "Metoda Siłowa" i "Dynamiczne Programowanie" (Kadane-a) wersje
|
* `A` [Maksymalna Podtablica](src/algorithms/sets/maximum-subarray) - "Metoda Siłowa" i "Dynamiczne Programowanie" (Kadane-a) wersje
|
||||||
* `A` [Suma Kombinacji](src/algorithms/sets/combination-sum) -
|
* `A` [Suma Kombinacji](src/algorithms/sets/combination-sum) -
|
||||||
znajdź wszystkie kombinacje, które tworzą określoną sumę
|
znajdź wszystkie kombinacje, które tworzą określoną sumę
|
||||||
* **Łańcuchy**
|
* **Łańcuchy**
|
||||||
* `B` [Odległość Hamminga](src/algorithms/string/hamming-distance) - liczba pozycji, w których symbole są różne
|
* `B` [Odległość Hamminga](src/algorithms/string/hamming-distance) - liczba pozycji, w których symbole są różne
|
||||||
@ -120,26 +120,26 @@ znajdź wszystkie kombinacje, które tworzą określoną sumę
|
|||||||
* `A` [Algorytm Floyd-Warshalla](src/algorithms/graph/floyd-warshall) - znajdź najkrótsze ścieżki między wszystkimi parami wierzchołków
|
* `A` [Algorytm Floyd-Warshalla](src/algorithms/graph/floyd-warshall) - znajdź najkrótsze ścieżki między wszystkimi parami wierzchołków
|
||||||
* `A` [Detect Cycle](src/algorithms/graph/detect-cycle) - zarówno dla wykresów skierowanych, jak i nieukierunkowanych(wersje oparte na DFS i Rozłączny Zestaw)
|
* `A` [Detect Cycle](src/algorithms/graph/detect-cycle) - zarówno dla wykresów skierowanych, jak i nieukierunkowanych(wersje oparte na DFS i Rozłączny Zestaw)
|
||||||
* `A` [Algorytm Prima](src/algorithms/graph/prim) - znalezienie Minimalnego Drzewa Opinającego (MST) dla ważonego nieukierunkowanego wykresu
|
* `A` [Algorytm Prima](src/algorithms/graph/prim) - znalezienie Minimalnego Drzewa Opinającego (MST) dla ważonego nieukierunkowanego wykresu
|
||||||
* `A` [Sortowanie Topologiczne](src/algorithms/graph/topological-sorting) - metoda DFS
|
* `A` [Sortowanie Topologiczne](src/algorithms/graph/topological-sorting) - metoda DFS
|
||||||
* `A` [Punkty Artykulacji](src/algorithms/graph/articulation-points) - Algorytm Tarjana (oparty o DFS)
|
* `A` [Punkty Artykulacji](src/algorithms/graph/articulation-points) - Algorytm Tarjana (oparty o DFS)
|
||||||
* `A` [Mosty](src/algorithms/graph/bridges) - Oparty na algorytmie DFS
|
* `A` [Mosty](src/algorithms/graph/bridges) - Oparty na algorytmie DFS
|
||||||
* `A` [Ścieżka Euleriana i Obwód Euleriana](src/algorithms/graph/eulerian-path) - Algorytm Fleurya - Odwiedź każdą krawędź dokładnie raz
|
* `A` [Ścieżka Euleriana i Obwód Euleriana](src/algorithms/graph/eulerian-path) - Algorytm Fleurya - Odwiedź każdą krawędź dokładnie raz
|
||||||
* `A` [Cykl Hamiltoniana](src/algorithms/graph/hamiltonian-cycle) - Odwiedź każdy wierzchołek dokładnie raz
|
* `A` [Cykl Hamiltoniana](src/algorithms/graph/hamiltonian-cycle) - Odwiedź każdy wierzchołek dokładnie raz
|
||||||
* `A` [Silnie Połączone Komponenty](src/algorithms/graph/strongly-connected-components) - Algorytm Kosaraja
|
* `A` [Silnie Połączone Komponenty](src/algorithms/graph/strongly-connected-components) - Algorytm Kosaraja
|
||||||
* `A` [Travelling Salesman Problem](src/algorithms/graph/travelling-salesman) - najkrótsza ścieżka która odwiedza każde miasto i wraca miasta początkującego
|
* `A` [Travelling Salesman Problem](src/algorithms/graph/travelling-salesman) - najkrótsza ścieżka która odwiedza każde miasto i wraca miasta początkującego
|
||||||
* **Niezkategorizowane**
|
* **Niezkategorizowane**
|
||||||
* `B` [Wieża Hanoi](src/algorithms/uncategorized/hanoi-tower)
|
* `B` [Wieża Hanoi](src/algorithms/uncategorized/hanoi-tower)
|
||||||
* `B` [Kwadratowa Matryca Obrotu](src/algorithms/uncategorized/square-matrix-rotation) - algorytm w miejscu
|
* `B` [Kwadratowa Matryca Obrotu](src/algorithms/uncategorized/square-matrix-rotation) - algorytm w miejscu
|
||||||
* `B` [Jump Game](src/algorithms/uncategorized/jump-game) - cofanie, dynamiczne programowanie (od góry do dołu + od dołu do góry) i przykłady chciwego
|
* `B` [Jump Game](src/algorithms/uncategorized/jump-game) - cofanie, dynamiczne programowanie (od góry do dołu + od dołu do góry) i przykłady chciwego
|
||||||
* `B` [Unikatowe Ścieżki](src/algorithms/uncategorized/unique-paths) - cofanie, dynamiczne programowanie i przykłady oparte na Trójkącie Pascala
|
* `B` [Unikatowe Ścieżki](src/algorithms/uncategorized/unique-paths) - cofanie, dynamiczne programowanie i przykłady oparte na Trójkącie Pascala
|
||||||
* `A` [Problem N-Queens](src/algorithms/uncategorized/n-queens)
|
* `A` [Problem N-Queens](src/algorithms/uncategorized/n-queens)
|
||||||
* `A` [Knight's Tour](src/algorithms/uncategorized/knight-tour)
|
* `A` [Knight's Tour](src/algorithms/uncategorized/knight-tour)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Algorytmy według paradygmatu
|
### Algorytmy według paradygmatu
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Paradygmat algorytmiczny jest ogólną metodą lub podejściem, które jest
|
Paradygmat algorytmiczny jest ogólną metodą lub podejściem, które jest
|
||||||
podstawą projektowania klasy algorytmów. Jest abstrakcją wyższą niż
|
podstawą projektowania klasy algorytmów. Jest abstrakcją wyższą niż
|
||||||
pojęcie algorytmu, podobnie jak algorytm jest abstrakcją wyższą niż
|
pojęcie algorytmu, podobnie jak algorytm jest abstrakcją wyższą niż
|
||||||
program komputerowy.
|
program komputerowy.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
* **Metoda Siłowa** - Sprawdza wszystkie możliwosci i wybiera najlepsze rozwiązanie.
|
* **Metoda Siłowa** - Sprawdza wszystkie możliwosci i wybiera najlepsze rozwiązanie.
|
||||||
@ -149,7 +149,7 @@ program komputerowy.
|
|||||||
* **Chciwy** - wybierz najlepszą opcję w obecnym czasie, bez względu na przyszłość
|
* **Chciwy** - wybierz najlepszą opcję w obecnym czasie, bez względu na przyszłość
|
||||||
* `B` [Jump Game](src/algorithms/uncategorized/jump-game)
|
* `B` [Jump Game](src/algorithms/uncategorized/jump-game)
|
||||||
* `A` [Niezwiązany Problem Knapsacka ](src/algorithms/sets/knapsack-problem)
|
* `A` [Niezwiązany Problem Knapsacka ](src/algorithms/sets/knapsack-problem)
|
||||||
* `A` [Algorytm Dijkstry](src/algorithms/graph/dijkstra) -
|
* `A` [Algorytm Dijkstry](src/algorithms/graph/dijkstra) -
|
||||||
znalezienie najkrótszej ścieżki do wszystkich wierzchołków grafu
|
znalezienie najkrótszej ścieżki do wszystkich wierzchołków grafu
|
||||||
* `A` [Algorytm Prima](src/algorithms/graph/prim) - znalezienie Minimalnego Drzewa Opinającego (MST) dla ważonego nieukierunkowanego wykresu
|
* `A` [Algorytm Prima](src/algorithms/graph/prim) - znalezienie Minimalnego Drzewa Opinającego (MST) dla ważonego nieukierunkowanego wykresu
|
||||||
* `A` [Algorytm Kruskala](src/algorithms/graph/kruskal) - znalezienie Minimalnego Drzewa Opinającego (MST) dla ważonego nieukierunkowanego wykresu
|
* `A` [Algorytm Kruskala](src/algorithms/graph/kruskal) - znalezienie Minimalnego Drzewa Opinającego (MST) dla ważonego nieukierunkowanego wykresu
|
||||||
@ -178,7 +178,7 @@ znalezienie najkrótszej ścieżki do wszystkich wierzchołków grafu
|
|||||||
* `A` [Partycja Całkowita](src/algorithms/math/integer-partition)
|
* `A` [Partycja Całkowita](src/algorithms/math/integer-partition)
|
||||||
* `A` [Maksymalne Podtablice](src/algorithms/sets/maximum-subarray)
|
* `A` [Maksymalne Podtablice](src/algorithms/sets/maximum-subarray)
|
||||||
* `A` [Algorytm Bellman-Forda](src/algorithms/graph/bellman-ford) - znalezienie najkrótszej ścieżki wszystkich wierzchołków wykresu
|
* `A` [Algorytm Bellman-Forda](src/algorithms/graph/bellman-ford) - znalezienie najkrótszej ścieżki wszystkich wierzchołków wykresu
|
||||||
* `A` [Algorytm Floyd-Warshalla](src/algorithms/graph/floyd-warshall) -
|
* `A` [Algorytm Floyd-Warshalla](src/algorithms/graph/floyd-warshall) -
|
||||||
znajdź najkrótsze ścieżki między wszystkimi parami wierzchołków
|
znajdź najkrótsze ścieżki między wszystkimi parami wierzchołków
|
||||||
* `A` [Dopasowanie Wyrażeń Regularnych](src/algorithms/string/regular-expression-matching)
|
* `A` [Dopasowanie Wyrażeń Regularnych](src/algorithms/string/regular-expression-matching)
|
||||||
* **Algorytm z nawrotami** - podobny do metody siłowej, próbuje wygenerować wszystkie możliwe rozwiązania, jednak za każdym razem generujesz następne rozwiązanie które testujesz
|
* **Algorytm z nawrotami** - podobny do metody siłowej, próbuje wygenerować wszystkie możliwe rozwiązania, jednak za każdym razem generujesz następne rozwiązanie które testujesz
|
||||||
@ -192,7 +192,7 @@ jeżeli zaspokaja wszystkie warunki, tylko wtedy generuje kolejne rozwiązania.
|
|||||||
* **Metoda Podziału i Ograniczeń** - Pamięta o niskonakładowym rozwiązaniu znalezionym na każdym etapie szukania nawrotu,
|
* **Metoda Podziału i Ograniczeń** - Pamięta o niskonakładowym rozwiązaniu znalezionym na każdym etapie szukania nawrotu,
|
||||||
używa kosztu niskonakładowego kosztu, które dotychczas zostało znalezione jako niska granica najmniejszego kosztu
|
używa kosztu niskonakładowego kosztu, które dotychczas zostało znalezione jako niska granica najmniejszego kosztu
|
||||||
do rozwiązanie problemu, aby odrzucić cząstkowe rozwiązania o kosztach większych niż niskonakładowe
|
do rozwiązanie problemu, aby odrzucić cząstkowe rozwiązania o kosztach większych niż niskonakładowe
|
||||||
rozwiązanie znalezione do tej pory.
|
rozwiązanie znalezione do tej pory.
|
||||||
Zazwyczan trajektoria BFS, w połączeniu z trajektorią Przeszukiwania W Głąb (DFS) drzewa przestrzeni stanów jest użyte.
|
Zazwyczan trajektoria BFS, w połączeniu z trajektorią Przeszukiwania W Głąb (DFS) drzewa przestrzeni stanów jest użyte.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Jak używać repozytorium
|
## Jak używać repozytorium
|
||||||
@ -225,7 +225,7 @@ npm test -- 'LinkedList'
|
|||||||
Możesz pociwiczyć ze strukturą danych i algorytmami w `./src/playground/playground.js` zakartotekuj i napisz
|
Możesz pociwiczyć ze strukturą danych i algorytmami w `./src/playground/playground.js` zakartotekuj i napisz
|
||||||
testy do tego w `./src/playground/__test__/playground.test.js`.
|
testy do tego w `./src/playground/__test__/playground.test.js`.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Następnie uruchom następującą komendę w celu przetestowania czy twoje kod działa według oczekiwań:
|
Następnie uruchom następującą komendę w celu przetestowania czy twoje kod działa według oczekiwań:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
npm test -- 'playground'
|
npm test -- 'playground'
|
||||||
@ -239,7 +239,7 @@ npm test -- 'playground'
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
### Big O Notacja
|
### Big O Notacja
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Kolejność wzrastania algorytmów według Big O notacji.
|
Kolejność wzrastania algorytmów według Big O notacji.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||

|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@ -4,7 +4,7 @@
|
|||||||
[](https://codecov.io/gh/trekhleb/javascript-algorithms)
|
[](https://codecov.io/gh/trekhleb/javascript-algorithms)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Este repositório contém exemplos baseados em JavaScript de muitos
|
Este repositório contém exemplos baseados em JavaScript de muitos
|
||||||
algoritmos e estruturas de dados populares.
|
algoritmos e estruturas de dados populares.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Cada algoritmo e estrutura de dado possui seu próprio README
|
Cada algoritmo e estrutura de dado possui seu próprio README
|
||||||
com explicações relacionadas e links para leitura adicional (incluindo
|
com explicações relacionadas e links para leitura adicional (incluindo
|
||||||
@ -61,7 +61,7 @@ um conjunto de regras que define precisamente uma sequência de operações.
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
* **Matemática**
|
* **Matemática**
|
||||||
* `B` [Manipulação Bit](src/algorithms/math/bits) - set/get/update/clear bits, multiplicação / divisão por dois, tornar negativo etc.
|
* `B` [Manipulação Bit](src/algorithms/math/bits) - set/get/update/clear bits, multiplicação / divisão por dois, tornar negativo etc.
|
||||||
* `B` [Fatorial](src/algorithms/math/factorial)
|
* `B` [Fatorial](src/algorithms/math/factorial)
|
||||||
* `B` [Número de Fibonacci](src/algorithms/math/fibonacci)
|
* `B` [Número de Fibonacci](src/algorithms/math/fibonacci)
|
||||||
* `B` [Teste de Primalidade](src/algorithms/math/primality-test) (método de divisão experimental)
|
* `B` [Teste de Primalidade](src/algorithms/math/primality-test) (método de divisão experimental)
|
||||||
* `B` [Algoritmo Euclidiano](src/algorithms/math/euclidean-algorithm) - calcular o maior divisor comum (GCD)
|
* `B` [Algoritmo Euclidiano](src/algorithms/math/euclidean-algorithm) - calcular o maior divisor comum (GCD)
|
||||||
@ -119,7 +119,7 @@ um conjunto de regras que define precisamente uma sequência de operações.
|
|||||||
* `A` [Floyd-Warshall Algorithm](src/algorithms/graph/floyd-warshall) - encontrar caminhos mais curtos entre todos os pares de vértices
|
* `A` [Floyd-Warshall Algorithm](src/algorithms/graph/floyd-warshall) - encontrar caminhos mais curtos entre todos os pares de vértices
|
||||||
* `A` [Detect Cycle](src/algorithms/graph/detect-cycle) - para gráficos direcionados e não direcionados (versões baseadas em DFS e Conjunto Disjuntivo)
|
* `A` [Detect Cycle](src/algorithms/graph/detect-cycle) - para gráficos direcionados e não direcionados (versões baseadas em DFS e Conjunto Disjuntivo)
|
||||||
* `A` [Prim’s Algorithm](src/algorithms/graph/prim) - encontrando Árvore Mínima de Abrangência (MST) para grafo não direcionado ponderado
|
* `A` [Prim’s Algorithm](src/algorithms/graph/prim) - encontrando Árvore Mínima de Abrangência (MST) para grafo não direcionado ponderado
|
||||||
* `A` [Topological Sorting](src/algorithms/graph/topological-sorting) - Métodos DFS
|
* `A` [Topological Sorting](src/algorithms/graph/topological-sorting) - Métodos DFS
|
||||||
* `A` [Articulation Points](src/algorithms/graph/articulation-points) -O algoritmo de Tarjan (baseado em DFS)
|
* `A` [Articulation Points](src/algorithms/graph/articulation-points) -O algoritmo de Tarjan (baseado em DFS)
|
||||||
* `A` [Bridges](src/algorithms/graph/bridges) - Algoritmo baseado em DFS
|
* `A` [Bridges](src/algorithms/graph/bridges) - Algoritmo baseado em DFS
|
||||||
* `A` [Eulerian Path and Eulerian Circuit](src/algorithms/graph/eulerian-path) - Algoritmo de Fleury - Visite todas as bordas exatamente uma vez
|
* `A` [Eulerian Path and Eulerian Circuit](src/algorithms/graph/eulerian-path) - Algoritmo de Fleury - Visite todas as bordas exatamente uma vez
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@ -56,7 +56,7 @@ _Читать на других языках:_
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
* **Математика**
|
* **Математика**
|
||||||
* `B` [Битовые манипуляции](src/algorithms/math/bits) — получение/запись/сброс/обновление битов, умножение/деление на 2, сделать отрицательным и т.п.
|
* `B` [Битовые манипуляции](src/algorithms/math/bits) — получение/запись/сброс/обновление битов, умножение/деление на 2, сделать отрицательным и т.п.
|
||||||
* `B` [Факториал](src/algorithms/math/factorial)
|
* `B` [Факториал](src/algorithms/math/factorial)
|
||||||
* `B` [Числа Фибоначчи](src/algorithms/math/fibonacci) — классическое решение, решение в замкнутой форме
|
* `B` [Числа Фибоначчи](src/algorithms/math/fibonacci) — классическое решение, решение в замкнутой форме
|
||||||
* `B` [Тест простоты](src/algorithms/math/primality-test) (метод пробного деления)
|
* `B` [Тест простоты](src/algorithms/math/primality-test) (метод пробного деления)
|
||||||
* `B` [Алгоритм Евклида](src/algorithms/math/euclidean-algorithm) — нахождение наибольшего общего делителя (НОД)
|
* `B` [Алгоритм Евклида](src/algorithms/math/euclidean-algorithm) — нахождение наибольшего общего делителя (НОД)
|
||||||
@ -70,7 +70,7 @@ _Читать на других языках:_
|
|||||||
* `A` [Разбиение числа](src/algorithms/math/integer-partition)
|
* `A` [Разбиение числа](src/algorithms/math/integer-partition)
|
||||||
* `A` [Квадратный корень](src/algorithms/math/square-root) — метод Ньютона
|
* `A` [Квадратный корень](src/algorithms/math/square-root) — метод Ньютона
|
||||||
* `A` [Алгоритм Лю Хуэя](src/algorithms/math/liu-hui) — расчёт числа π с заданной точностью методом вписанных правильных многоугольников
|
* `A` [Алгоритм Лю Хуэя](src/algorithms/math/liu-hui) — расчёт числа π с заданной точностью методом вписанных правильных многоугольников
|
||||||
* `A` [Дискретное преобразование Фурье](src/algorithms/math/fourier-transform) — разложение временной функции (сигнала) на частотные составляющие
|
* `A` [Дискретное преобразование Фурье](src/algorithms/math/fourier-transform) — разложение временной функции (сигнала) на частотные составляющие
|
||||||
* **Множества**
|
* **Множества**
|
||||||
* `B` [Декартово произведение](src/algorithms/sets/cartesian-product) — результат перемножения множеств
|
* `B` [Декартово произведение](src/algorithms/sets/cartesian-product) — результат перемножения множеств
|
||||||
* `B` [Тасование Фишера — Йетса](src/algorithms/sets/fisher-yates) — создание случайных перестановок конечного множества
|
* `B` [Тасование Фишера — Йетса](src/algorithms/sets/fisher-yates) — создание случайных перестановок конечного множества
|
||||||
@ -135,7 +135,7 @@ _Читать на других языках:_
|
|||||||
* **Прочие алгоритмы**
|
* **Прочие алгоритмы**
|
||||||
* `B` [Ханойская башня](src/algorithms/uncategorized/hanoi-tower)
|
* `B` [Ханойская башня](src/algorithms/uncategorized/hanoi-tower)
|
||||||
* `B` [Поворот квадратной матрицы](src/algorithms/uncategorized/square-matrix-rotation) — используется дополнительная память
|
* `B` [Поворот квадратной матрицы](src/algorithms/uncategorized/square-matrix-rotation) — используется дополнительная память
|
||||||
* `B` [Прыжки](src/algorithms/uncategorized/jump-game) — на основе бэктрекинга, динамического программирования (сверху-вниз + снизу-вверх) и жадных алгоритмов
|
* `B` [Прыжки](src/algorithms/uncategorized/jump-game) — на основе бэктрекинга, динамического программирования (сверху-вниз + снизу-вверх) и жадных алгоритмов
|
||||||
* `B` [Поиск уникальных путей](src/algorithms/uncategorized/unique-paths) — на основе бэктрекинга, динамического программирования и треугольника Паскаля
|
* `B` [Поиск уникальных путей](src/algorithms/uncategorized/unique-paths) — на основе бэктрекинга, динамического программирования и треугольника Паскаля
|
||||||
* `B` [Подсчёт дождевой воды](src/algorithms/uncategorized/rain-terraces) — на основе перебора и динамического программирования
|
* `B` [Подсчёт дождевой воды](src/algorithms/uncategorized/rain-terraces) — на основе перебора и динамического программирования
|
||||||
* `B` [Задача о рекурсивной лестнице](src/algorithms/uncategorized/recursive-staircase) — подсчёт количества путей, по которым можно достичь верха лестницы (4 способа)
|
* `B` [Задача о рекурсивной лестнице](src/algorithms/uncategorized/recursive-staircase) — подсчёт количества путей, по которым можно достичь верха лестницы (4 способа)
|
||||||
@ -153,7 +153,7 @@ _Читать на других языках:_
|
|||||||
* `A` [Максимальный подмассив](src/algorithms/sets/maximum-subarray)
|
* `A` [Максимальный подмассив](src/algorithms/sets/maximum-subarray)
|
||||||
* `A` [Задача коммивояжёра](src/algorithms/graph/travelling-salesman) — кратчайший маршрут, проходящий через указанные города с последующим возвратом в исходный город
|
* `A` [Задача коммивояжёра](src/algorithms/graph/travelling-salesman) — кратчайший маршрут, проходящий через указанные города с последующим возвратом в исходный город
|
||||||
* `A` [Дискретное преобразование Фурье](src/algorithms/math/fourier-transform) — разложение временной функции (сигнала) на частотные составляющие
|
* `A` [Дискретное преобразование Фурье](src/algorithms/math/fourier-transform) — разложение временной функции (сигнала) на частотные составляющие
|
||||||
* **Жадные алгоритмы** — принятие локально оптимальных решений с учётом допущения об оптимальности конечного решения
|
* **Жадные алгоритмы** — принятие локально оптимальных решений с учётом допущения об оптимальности конечного решения
|
||||||
* `B` [Прыжки](src/algorithms/uncategorized/jump-game)
|
* `B` [Прыжки](src/algorithms/uncategorized/jump-game)
|
||||||
* `A` [Задача о неограниченном рюкзаке](src/algorithms/sets/knapsack-problem)
|
* `A` [Задача о неограниченном рюкзаке](src/algorithms/sets/knapsack-problem)
|
||||||
* `A` [Алгоритм Дейкстры](src/algorithms/graph/dijkstra) — нахождение кратчайших путей от одной из вершин графа до всех остальных
|
* `A` [Алгоритм Дейкстры](src/algorithms/graph/dijkstra) — нахождение кратчайших путей от одной из вершин графа до всех остальных
|
||||||
@ -228,7 +228,7 @@ npm test -- 'LinkedList'
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
**Песочница**
|
**Песочница**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Вы можете экспериментировать с алгоритмами и структурами данных в файле `./src/playground/playground.js`
|
Вы можете экспериментировать с алгоритмами и структурами данных в файле `./src/playground/playground.js`
|
||||||
(файл `./src/playground/__test__/playground.test.js` предназначен для написания тестов).
|
(файл `./src/playground/__test__/playground.test.js` предназначен для написания тестов).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Для проверки работоспособности вашего кода используйте команду:
|
Для проверки работоспособности вашего кода используйте команду:
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@ -6,8 +6,8 @@
|
|||||||
Bu repository JavaScript'e ait popüler
|
Bu repository JavaScript'e ait popüler
|
||||||
algoritma ve veri yapılarını içermektedir.
|
algoritma ve veri yapılarını içermektedir.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Her bir algoritma ve veri yapısı kendine
|
Her bir algoritma ve veri yapısı kendine
|
||||||
ait açıklama ve videoya sahip README dosyası içerir.
|
ait açıklama ve videoya sahip README dosyası içerir.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
_Read this in other languages:_
|
_Read this in other languages:_
|
||||||
[_简体中文_](README.zh-CN.md),
|
[_简体中文_](README.zh-CN.md),
|
||||||
@ -21,7 +21,7 @@ _Read this in other languages:_
|
|||||||
[_Русский_](README.ru-RU.md),
|
[_Русский_](README.ru-RU.md),
|
||||||
[_Italiana_](README.it-IT.md)
|
[_Italiana_](README.it-IT.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
*☝ Not, bu proje araştırma ve öğrenme amacı ile yapılmış
|
*☝ Not, bu proje araştırma ve öğrenme amacı ile yapılmış
|
||||||
olup üretim için **yaplılmamıştır**.*
|
olup üretim için **yaplılmamıştır**.*
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Veri Yapıları
|
## Veri Yapıları
|
||||||
@ -63,7 +63,7 @@ bir işlem dizisini kesin olarak tanımlayan bir dizi kural.
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
* **Matematik**
|
* **Matematik**
|
||||||
* `B` [Bit Manipülasyonu](src/algorithms/math/bits) - set/get/update/clear bits, multiplication/division by two, make negative etc.
|
* `B` [Bit Manipülasyonu](src/algorithms/math/bits) - set/get/update/clear bits, multiplication/division by two, make negative etc.
|
||||||
* `B` [Faktöriyel](src/algorithms/math/factorial)
|
* `B` [Faktöriyel](src/algorithms/math/factorial)
|
||||||
* `B` [Fibonacci Sayısı](src/algorithms/math/fibonacci) - klasik ve kapalı-form versiyonları
|
* `B` [Fibonacci Sayısı](src/algorithms/math/fibonacci) - klasik ve kapalı-form versiyonları
|
||||||
* `B` [Asallık Testi](src/algorithms/math/primality-test) (trial division method)
|
* `B` [Asallık Testi](src/algorithms/math/primality-test) (trial division method)
|
||||||
* `B` [Öklid Algoritması](src/algorithms/math/euclidean-algorithm) - En büyük ortak bölen hesaplama (EBOB)
|
* `B` [Öklid Algoritması](src/algorithms/math/euclidean-algorithm) - En büyük ortak bölen hesaplama (EBOB)
|
||||||
@ -143,8 +143,8 @@ bir işlem dizisini kesin olarak tanımlayan bir dizi kural.
|
|||||||
* **Kategoriye Ayrılmayanlar**
|
* **Kategoriye Ayrılmayanlar**
|
||||||
* `B` [Tower of Hanoi](src/algorithms/uncategorized/hanoi-tower)
|
* `B` [Tower of Hanoi](src/algorithms/uncategorized/hanoi-tower)
|
||||||
* `B` [Square Matrix Rotation](src/algorithms/uncategorized/square-matrix-rotation) - in-place algorithm
|
* `B` [Square Matrix Rotation](src/algorithms/uncategorized/square-matrix-rotation) - in-place algorithm
|
||||||
* `B` [Jump Game](src/algorithms/uncategorized/jump-game) - backtracking, dynamic programming (top-down + bottom-up) and greedy examples
|
* `B` [Jump Game](src/algorithms/uncategorized/jump-game) - backtracking, dynamic programming (top-down + bottom-up) and greedy examples
|
||||||
* `B` [Unique Paths](src/algorithms/uncategorized/unique-paths) - backtracking, dynamic programming and Pascal's Triangle based examples
|
* `B` [Unique Paths](src/algorithms/uncategorized/unique-paths) - backtracking, dynamic programming and Pascal's Triangle based examples
|
||||||
* `B` [Rain Terraces](src/algorithms/uncategorized/rain-terraces) - trapping rain water problem (dynamic programming and brute force versions)
|
* `B` [Rain Terraces](src/algorithms/uncategorized/rain-terraces) - trapping rain water problem (dynamic programming and brute force versions)
|
||||||
* `B` [Recursive Staircase](src/algorithms/uncategorized/recursive-staircase) - tepeye ulaşmanın yollarını sayma (4 çözüm)
|
* `B` [Recursive Staircase](src/algorithms/uncategorized/recursive-staircase) - tepeye ulaşmanın yollarını sayma (4 çözüm)
|
||||||
* `A` [N-Queens Problem](src/algorithms/uncategorized/n-queens)
|
* `A` [N-Queens Problem](src/algorithms/uncategorized/n-queens)
|
||||||
@ -152,8 +152,8 @@ bir işlem dizisini kesin olarak tanımlayan bir dizi kural.
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
### Algoritmik Paradigma
|
### Algoritmik Paradigma
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Algoritmik paradigma, bir sınıfın tasarımının altında yatan genel bir yöntem veya yaklaşımdır.
|
Algoritmik paradigma, bir sınıfın tasarımının altında yatan genel bir yöntem veya yaklaşımdır.
|
||||||
Algoritma dizayn tekniği olarak düşünülebilir. Her bir altproblemi (subproblem) asıl problemle
|
Algoritma dizayn tekniği olarak düşünülebilir. Her bir altproblemi (subproblem) asıl problemle
|
||||||
benzerlik gösteren problemlere uygulanabilir.
|
benzerlik gösteren problemlere uygulanabilir.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
* **Brute Force** - mümkün olan tüm çözümleri tara ve en iyisini seç
|
* **Brute Force** - mümkün olan tüm çözümleri tara ve en iyisini seç
|
||||||
@ -198,7 +198,7 @@ benzerlik gösteren problemlere uygulanabilir.
|
|||||||
* `A` [Maximum Subarray](src/algorithms/sets/maximum-subarray)
|
* `A` [Maximum Subarray](src/algorithms/sets/maximum-subarray)
|
||||||
* `A` [Bellman-Ford Algorithm](src/algorithms/graph/bellman-ford) - tüm grafik köşelerine giden en kısa yolu bulmak
|
* `A` [Bellman-Ford Algorithm](src/algorithms/graph/bellman-ford) - tüm grafik köşelerine giden en kısa yolu bulmak
|
||||||
* `A` [Floyd-Warshall Algorithm](src/algorithms/graph/floyd-warshall) - tüm köşe çiftleri arasındaki en kısa yolları bulun
|
* `A` [Floyd-Warshall Algorithm](src/algorithms/graph/floyd-warshall) - tüm köşe çiftleri arasındaki en kısa yolları bulun
|
||||||
* `A` [Regular Expression Matching](src/algorithms/string/regular-expression-matching)
|
* `A` [Regular Expression Matching](src/algorithms/string/regular-expression-matching)
|
||||||
* **Backtracking** - brute forceye benzer, mümkün tüm sonuçları tara, ancak bir sonraki çözümü her ürettiğinizde test edersiniz
|
* **Backtracking** - brute forceye benzer, mümkün tüm sonuçları tara, ancak bir sonraki çözümü her ürettiğinizde test edersiniz
|
||||||
tüm koşulları karşılıyorsa ve ancak o zaman sonraki çözümleri üretmeye devam edin. Aksi takdirde, geri dönün ve farklı bir çözüm arayın(?).
|
tüm koşulları karşılıyorsa ve ancak o zaman sonraki çözümleri üretmeye devam edin. Aksi takdirde, geri dönün ve farklı bir çözüm arayın(?).
|
||||||
Normally the DFS traversal of state-space is being used.
|
Normally the DFS traversal of state-space is being used.
|
||||||
@ -242,7 +242,7 @@ npm test -- 'LinkedList'
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
**Deneme Alanı**
|
**Deneme Alanı**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
data-structures ve algorithms içerisinde `./src/playground/playground.js`
|
data-structures ve algorithms içerisinde `./src/playground/playground.js`
|
||||||
yazarak `./src/playground/__test__/playground.test.js` için test edebilirsin.
|
yazarak `./src/playground/__test__/playground.test.js` için test edebilirsin.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@ -310,4 +310,4 @@ Altta Big O notations ve farklı input boyutlarına karşın yapılmış perform
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
## Projeyi Destekleme
|
## Projeyi Destekleme
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Bu projeyi buradan destekleyebilirsiniz ❤️️ [GitHub](https://github.com/sponsors/trekhleb) veya ❤️️ [Patreon](https://www.patreon.com/trekhleb).
|
Bu projeyi buradan destekleyebilirsiniz ❤️️ [GitHub](https://github.com/sponsors/trekhleb) veya ❤️️ [Patreon](https://www.patreon.com/trekhleb).
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@ -25,4 +25,14 @@ module.exports = {
|
|||||||
// It is reflected in properties such as location.href.
|
// It is reflected in properties such as location.href.
|
||||||
// @see: https://github.com/facebook/jest/issues/6769
|
// @see: https://github.com/facebook/jest/issues/6769
|
||||||
testURL: 'http://localhost/',
|
testURL: 'http://localhost/',
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// @see: https://jestjs.io/docs/en/configuration#coveragethreshold-object
|
||||||
|
coverageThreshold: {
|
||||||
|
global: {
|
||||||
|
statements: 100,
|
||||||
|
branches: 95,
|
||||||
|
functions: 100,
|
||||||
|
lines: 100,
|
||||||
|
},
|
||||||
|
},
|
||||||
};
|
};
|
||||||
|
|||||||
41
src/algorithms/ml/knn/README.md
Normal file
41
src/algorithms/ml/knn/README.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
|
|||||||
|
# k-Nearest Neighbors Algorithm
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
The **k-nearest neighbors algorithm (k-NN)** is a supervised Machine Learning algorithm. It's a classification algorithm, determining the class of a sample vector using a sample data.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
In k-NN classification, the output is a class membership. An object is classified by a plurality vote of its neighbors, with the object being assigned to the class most common among its `k` nearest neighbors (`k` is a positive integer, typically small). If `k = 1`, then the object is simply assigned to the class of that single nearest neighbor.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
The idea is to calculate the similarity between two data points on the basis of a distance metric. [Euclidean distance](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Euclidean_distance) is used mostly for this task.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
_Image source: [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Euclidean_distance)_
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
The algorithm is as follows:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
1. Check for errors like invalid data/labels.
|
||||||
|
2. Calculate the euclidean distance of all the data points in training data with the classification point
|
||||||
|
3. Sort the distances of points along with their classes in ascending order
|
||||||
|
4. Take the initial `K` classes and find the mode to get the most similar class
|
||||||
|
5. Report the most similar class
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Here is a visualization of k-NN classification for better understanding:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
_Image source: [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/K-nearest_neighbors_algorithm)_
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
The test sample (green dot) should be classified either to blue squares or to red triangles. If `k = 3` (solid line circle) it is assigned to the red triangles because there are `2` triangles and only `1` square inside the inner circle. If `k = 5` (dashed line circle) it is assigned to the blue squares (`3` squares vs. `2` triangles inside the outer circle).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Another k-NN classification example:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
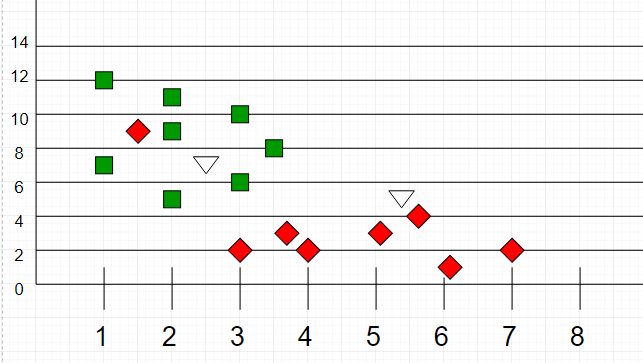
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
_Image source: [GeeksForGeeks](https://media.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/uploads/graph2-2.png)_
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Here, as we can see, the classification of unknown points will be judged by their proximity to other points.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
It is important to note that `K` is preferred to have odd values in order to break ties. Usually `K` is taken as `3` or `5`.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## References
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- [k-nearest neighbors algorithm on Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/K-nearest_neighbors_algorithm)
|
||||||
71
src/algorithms/ml/knn/__test__/knn.test.js
Normal file
71
src/algorithms/ml/knn/__test__/knn.test.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,71 @@
|
|||||||
|
import kNN from '../kNN';
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
describe('kNN', () => {
|
||||||
|
it('should throw an error on invalid data', () => {
|
||||||
|
expect(() => {
|
||||||
|
kNN();
|
||||||
|
}).toThrowError('Either dataSet or labels or toClassify were not set');
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
it('should throw an error on invalid labels', () => {
|
||||||
|
const noLabels = () => {
|
||||||
|
kNN([[1, 1]]);
|
||||||
|
};
|
||||||
|
expect(noLabels).toThrowError('Either dataSet or labels or toClassify were not set');
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
it('should throw an error on not giving classification vector', () => {
|
||||||
|
const noClassification = () => {
|
||||||
|
kNN([[1, 1]], [1]);
|
||||||
|
};
|
||||||
|
expect(noClassification).toThrowError('Either dataSet or labels or toClassify were not set');
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
it('should throw an error on not giving classification vector', () => {
|
||||||
|
const inconsistent = () => {
|
||||||
|
kNN([[1, 1]], [1], [1]);
|
||||||
|
};
|
||||||
|
expect(inconsistent).toThrowError('Inconsistent vector lengths');
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
it('should find the nearest neighbour', () => {
|
||||||
|
let dataSet;
|
||||||
|
let labels;
|
||||||
|
let toClassify;
|
||||||
|
let expectedClass;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
dataSet = [[1, 1], [2, 2]];
|
||||||
|
labels = [1, 2];
|
||||||
|
toClassify = [1, 1];
|
||||||
|
expectedClass = 1;
|
||||||
|
expect(kNN(dataSet, labels, toClassify)).toBe(expectedClass);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
dataSet = [[1, 1], [6, 2], [3, 3], [4, 5], [9, 2], [2, 4], [8, 7]];
|
||||||
|
labels = [1, 2, 1, 2, 1, 2, 1];
|
||||||
|
toClassify = [1.25, 1.25];
|
||||||
|
expectedClass = 1;
|
||||||
|
expect(kNN(dataSet, labels, toClassify)).toBe(expectedClass);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
dataSet = [[1, 1], [6, 2], [3, 3], [4, 5], [9, 2], [2, 4], [8, 7]];
|
||||||
|
labels = [1, 2, 1, 2, 1, 2, 1];
|
||||||
|
toClassify = [1.25, 1.25];
|
||||||
|
expectedClass = 2;
|
||||||
|
expect(kNN(dataSet, labels, toClassify, 5)).toBe(expectedClass);
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
it('should find the nearest neighbour with equal distances', () => {
|
||||||
|
const dataSet = [[0, 0], [1, 1], [0, 2]];
|
||||||
|
const labels = [1, 3, 3];
|
||||||
|
const toClassify = [0, 1];
|
||||||
|
const expectedClass = 3;
|
||||||
|
expect(kNN(dataSet, labels, toClassify)).toBe(expectedClass);
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
it('should find the nearest neighbour in 3D space', () => {
|
||||||
|
const dataSet = [[0, 0, 0], [0, 1, 1], [0, 0, 2]];
|
||||||
|
const labels = [1, 3, 3];
|
||||||
|
const toClassify = [0, 0, 1];
|
||||||
|
const expectedClass = 3;
|
||||||
|
expect(kNN(dataSet, labels, toClassify)).toBe(expectedClass);
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
77
src/algorithms/ml/knn/kNN.js
Normal file
77
src/algorithms/ml/knn/kNN.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,77 @@
|
|||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* Calculates calculate the euclidean distance between 2 vectors.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* @param {number[]} x1
|
||||||
|
* @param {number[]} x2
|
||||||
|
* @returns {number}
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
function euclideanDistance(x1, x2) {
|
||||||
|
// Checking for errors.
|
||||||
|
if (x1.length !== x2.length) {
|
||||||
|
throw new Error('Inconsistent vector lengths');
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
// Calculate the euclidean distance between 2 vectors and return.
|
||||||
|
let squaresTotal = 0;
|
||||||
|
for (let i = 0; i < x1.length; i += 1) {
|
||||||
|
squaresTotal += (x1[i] - x2[i]) ** 2;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return Number(Math.sqrt(squaresTotal).toFixed(2));
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
/**
|
||||||
|
* Classifies the point in space based on k-nearest neighbors algorithm.
|
||||||
|
*
|
||||||
|
* @param {number[][]} dataSet - array of data points, i.e. [[0, 1], [3, 4], [5, 7]]
|
||||||
|
* @param {number[]} labels - array of classes (labels), i.e. [1, 1, 2]
|
||||||
|
* @param {number[]} toClassify - the point in space that needs to be classified, i.e. [5, 4]
|
||||||
|
* @param {number} k - number of nearest neighbors which will be taken into account (preferably odd)
|
||||||
|
* @return {number} - the class of the point
|
||||||
|
*/
|
||||||
|
export default function kNN(
|
||||||
|
dataSet,
|
||||||
|
labels,
|
||||||
|
toClassify,
|
||||||
|
k = 3,
|
||||||
|
) {
|
||||||
|
if (!dataSet || !labels || !toClassify) {
|
||||||
|
throw new Error('Either dataSet or labels or toClassify were not set');
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// Calculate distance from toClassify to each point for all dimensions in dataSet.
|
||||||
|
// Store distance and point's label into distances list.
|
||||||
|
const distances = [];
|
||||||
|
for (let i = 0; i < dataSet.length; i += 1) {
|
||||||
|
distances.push({
|
||||||
|
dist: euclideanDistance(dataSet[i], toClassify),
|
||||||
|
label: labels[i],
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// Sort distances list (from closer point to further ones).
|
||||||
|
// Take initial k values, count with class index
|
||||||
|
const kNearest = distances.sort((a, b) => {
|
||||||
|
if (a.dist === b.dist) {
|
||||||
|
return 0;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return a.dist < b.dist ? -1 : 1;
|
||||||
|
}).slice(0, k);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// Count the number of instances of each class in top k members.
|
||||||
|
const labelsCounter = {};
|
||||||
|
let topClass = 0;
|
||||||
|
let topClassCount = 0;
|
||||||
|
for (let i = 0; i < kNearest.length; i += 1) {
|
||||||
|
if (kNearest[i].label in labelsCounter) {
|
||||||
|
labelsCounter[kNearest[i].label] += 1;
|
||||||
|
} else {
|
||||||
|
labelsCounter[kNearest[i].label] = 1;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
if (labelsCounter[kNearest[i].label] > topClassCount) {
|
||||||
|
topClassCount = labelsCounter[kNearest[i].label];
|
||||||
|
topClass = kNearest[i].label;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// Return the class with highest count.
|
||||||
|
return topClass;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
@ -1,11 +1,14 @@
|
|||||||
# Bubble Sort
|
# Bubble Sort
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Bubble sort, sometimes referred to as sinking sort, is a
|
_Read this in other languages:_
|
||||||
simple sorting algorithm that repeatedly steps through
|
[_Português_](README.pt-BR.md)
|
||||||
the list to be sorted, compares each pair of adjacent
|
|
||||||
items and swaps them if they are in the wrong order
|
Bubble sort, sometimes referred to as sinking sort, is a
|
||||||
|
simple sorting algorithm that repeatedly steps through
|
||||||
|
the list to be sorted, compares each pair of adjacent
|
||||||
|
items and swaps them if they are in the wrong order
|
||||||
(ascending or descending arrangement). The pass through
|
(ascending or descending arrangement). The pass through
|
||||||
the list is repeated until no swaps are needed, which
|
the list is repeated until no swaps are needed, which
|
||||||
indicates that the list is sorted.
|
indicates that the list is sorted.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||

|

|
||||||
|
|||||||
17
src/algorithms/sorting/bubble-sort/README.pt-BR.md
Normal file
17
src/algorithms/sorting/bubble-sort/README.pt-BR.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
|
|||||||
|
# Bubble Sort
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
O bubble sort, ou ordenação por flutuação (literalmente "por bolha"), é um algoritmo de ordenação dos mais simples. A ideia é percorrer o vetor diversas vezes, e a cada passagem fazer flutuar para o topo o maior elemento da sequência. Essa movimentação lembra a forma como as bolhas em um tanque de água procuram seu próprio nível, e disso vem o nome do algoritmo.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Complexity
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
| Name | Best | Average | Worst | Memory | Stable | Comments |
|
||||||
|
| --------------------- | :-------------: | :-----------------: | :-----------------: | :-------: | :-------: | :-------- |
|
||||||
|
| **Bubble sort** | n | n<sup>2</sup> | n<sup>2</sup> | 1 | Yes | |
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## References
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- [Wikipedia](https://pt.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bubble_sort)
|
||||||
|
- [YouTube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6Gv8vg0kcHc&index=27&t=0s&list=PLLXdhg_r2hKA7DPDsunoDZ-Z769jWn4R8)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@ -51,7 +51,7 @@ Remove(head, value)
|
|||||||
return true
|
return true
|
||||||
end if
|
end if
|
||||||
n ← head.next
|
n ← head.next
|
||||||
while n = ø and value = n.value
|
while n = ø and value !== n.value
|
||||||
n ← n.next
|
n ← n.next
|
||||||
end while
|
end while
|
||||||
if n = tail
|
if n = tail
|
||||||
|
|||||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user